Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven to be an effective treatment for dermatillomania, a condition characterized by repetitive skin picking. CBT addresses the underlying thoughts and feelings that contribute to this behavior, helping individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce urges to pick. By focusing on changing thought patterns and behaviors, those affected can experience significant relief and improve their quality of life.
This therapeutic approach equips individuals with practical strategies to manage triggers and build emotional resilience. Through guided sessions with a qualified therapist, patients learn to identify and challenge the beliefs driving their skin picking habits. As they progress, they often find themselves regaining control over their impulses and fostering a more positive self-image.
For anyone struggling with dermatillomania, exploring CBT as a treatment option can be a transformative step. Understanding how this therapy works is essential for those seeking effective solutions to break free from these compulsions.
Understanding Dermatillomania
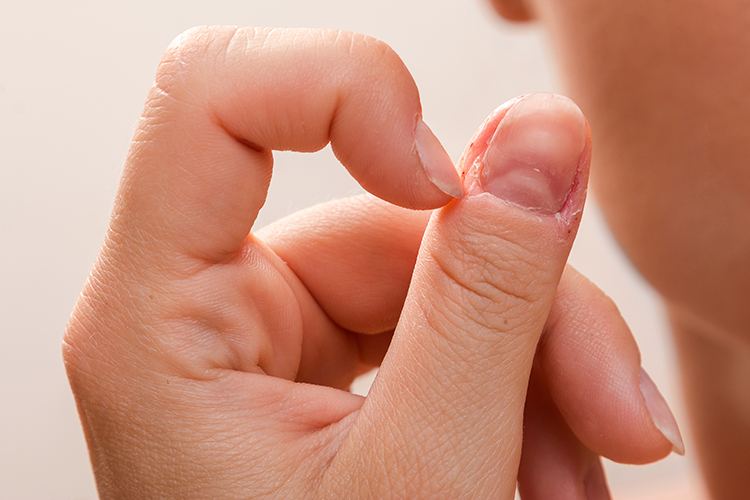
Dermatillomania, or skin picking disorder, is a behavioral condition that leads individuals to compulsively pick at their skin, resulting in physical damage. Understanding this condition involves defining it, exploring its prevalence, and identifying potential causes and risk factors.
Definition and Symptoms
Dermatillomania is classified as a body-focused repetitive behavior (BFRB). Individuals diagnosed with this condition repeatedly pick at their skin, often leading to noticeable lesions or scars.
Symptoms may include:
- Repeatedly picking at skin despite attempts to stop.
- Hiding affected areas of skin.
- Engaging in skin picking during moments of stress or boredom.
This behavior can cause significant emotional distress and impact daily functioning.
Prevalence and Demographics
Research indicates that dermatillomania affects approximately 1-5% of the population. It can occur in both genders but is more frequently reported among females.
Demographics show:
- Age of onset: usually during adolescence.
- Comorbidity: high rates of anxiety and depression are often observed among those affected.
The condition spans various ethnicities and backgrounds, though many individuals remain undiagnosed due to stigma or lack of awareness.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of dermatillomania are not completely understood, but a mix of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors may contribute.
Some identified risk factors include:
- Family history of BFRBs or other mental health conditions.
- Personality traits such as perfectionism or high sensitivity to stress.
- Traumatic experiences or chronic stress can trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
Understanding these factors is essential for recognizing and addressing dermatillomania effectively.
CBT for Dermatillomania
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment for dermatillomania, also known as skin picking disorder. This method focuses on altering negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with skin picking to improve the individual’s quality of life.
Overview of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
CBT is a structured therapy that aims to modify unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. It involves identifying triggers that lead to skin picking and developing coping strategies.
Patients often work with a therapist to explore the thoughts and emotions tied to their urge to pick at their skin. The goal is to replace these compulsive behaviors with healthier habits.
This therapeutic approach is typically short-term and can be conducted in individual or group settings. Evidence suggests that CBT provides lasting results, even after therapy concludes.
CBT Techniques and Approaches
Several specific techniques are employed within CBT for dermatillomania. Habit reversal training is one such method, which helps individuals recognize their skin-picking behaviors and substitute them with alternative actions.
Another technique is exposure and response prevention (ERP). This involves gradually exposing the individual to situations that trigger their skin picking while helping them refrain from acting on those urges.
Cognitive restructuring is also important, as it helps patients challenge negative beliefs about their appearance and self-worth. Journaling and self-monitoring can track progress and increase awareness of triggers.
Effectiveness of CBT for Skin Picking
Research indicates that CBT is beneficial for individuals with dermatillomania. Many studies report a significant reduction in skin-picking behaviors among participants undergoing CBT.
Patients often experience improved emotional regulation and decreased anxiety related to skin picking. Assessments typically show sustained improvements even after treatment ends, indicating the durability of CBT results.
Effectiveness can vary based on the individual’s commitment and the severity of their condition. Overall, integrating CBT with other interventions can enhance treatment outcomes.
Integrating CBT into Treatment Plans
Integrating CBT into a comprehensive treatment plan involves collaboration among healthcare professionals. Coordination ensures that patients receive holistic care tailored to their needs.
A structured plan may include regular CBT sessions, homework assignments, and support for motivation. Patients can benefit from combining CBT with medication or other therapeutic approaches for comprehensive management.
Family involvement may also enhance support systems, creating a conducive environment for recovery. With proper integration, CBT can address the multifaceted nature of dermatillomania, fostering long-term success.