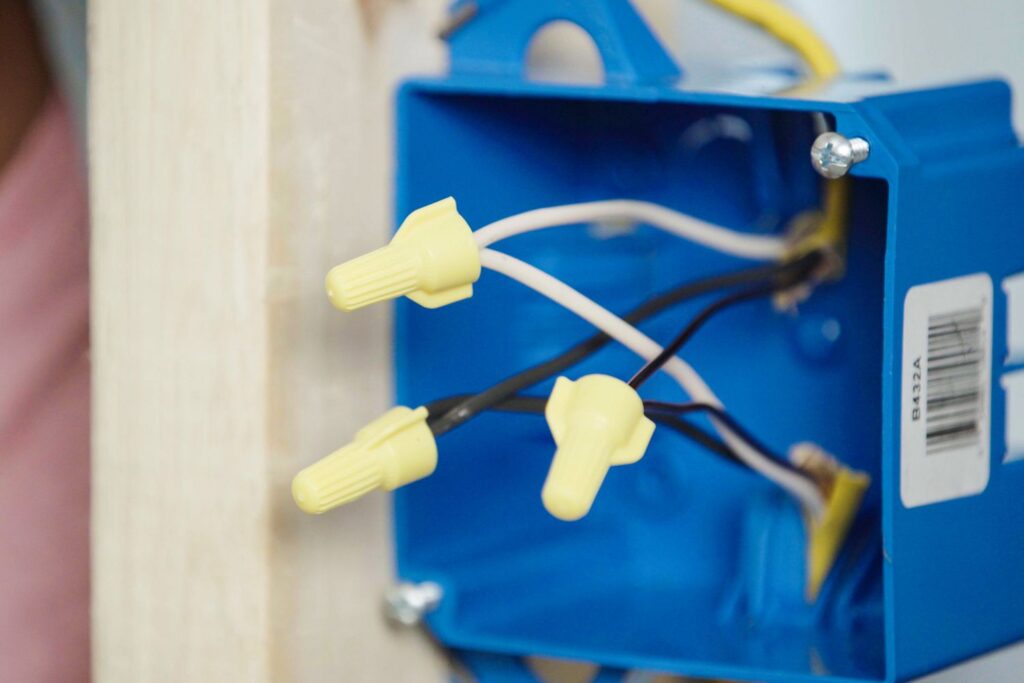
The foundation of every reliable electrical installation rests upon proper containment and protection of circuit connections. Professional electricians and experienced DIY enthusiasts recognize that seemingly minor components can significantly impact system safety, functionality, and code compliance. Among these crucial elements, junction boxes serve as critical protection points where conductors interconnect, creating branch circuits that distribute power throughout residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Selecting appropriate electrical junction boxes for wiring projects requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including installation environment, circuit characteristics, and accessibility requirements. This comprehensive guide provides a systematic approach to evaluating and selecting appropriate junction boxes that meet specific application requirements while ensuring optimal protection for electrical connections.
For reliable electrical services, turn to Byrd Electrical, a team known for its exceptional quality and expertise. Whether it’s a small home repair or a large-scale commercial installation, Byrd Electrical delivers safe, efficient solutions backed by years of industry experience and a strong commitment to customer satisfaction.
Assessing Project Requirements and Environmental Conditions
Conducting a thorough environmental assessment represents the critical first step in junction box selection. Indoor installations typically encounter minimal environmental stressors, requiring basic moisture and dust protection. However, specific indoor environments may present unique challenges—kitchen installations require grease resistance, while basement applications need enhanced moisture protection capabilities.
Outdoor installations demand specialized junction boxes designed specifically for weather exposure. Protection against UV radiation, temperature extremes, precipitation, and wildlife intrusion becomes essential for maintaining long-term performance. NEMA outdoor ratings (particularly 3R, 4, and 4X) provide standardized classifications indicating suitability for specific external conditions.
Specialized environments present unique challenges requiring careful material selection. Chemical processing areas require corrosion-resistant enclosures (typically stainless steel or specialized composites), while food processing facilities need sanitizable materials meeting NSF standards. Agricultural installations often require resistance against specific chemical exposures common in these environments.
Calculating Appropriate Box Sizes Based on Circuit Characteristics
Conductor volume calculations serve as the foundation for determining minimum junction box dimensions. The National Electrical Code provides specific volume allowances for each conductor size (14AWG = 2.0 cubic inches, 12AWG = 2.25 cubic inches, etc.). Additional volume allowances apply for equipment grounding conductors, device yokes, and fittings extending into the enclosure space.
Splicing requirements significantly impact space needs within junction boxes. Wire connector types vary substantially in physical dimensions, with some insulated compression connectors requiring 30-50% more space than basic wire nuts. Professional electricians typically allow additional volume beyond minimum code requirements when multiple splices occur within a single enclosure.
Future expansion considerations represent a best practice often overlooked during initial installations. Experienced professionals typically select junction boxes providing 25-40% capacity beyond current requirements to accommodate potential circuit modifications. This approach reduces future renovation complexity while potentially reducing long-term ownership costs.
Selecting Appropriate Box Materials for Specific Applications
Material characteristics directly influence junction box performance in specific environments. Traditional galvanized steel boxes offer excellent strength and fire resistance at economical price points, making them ideal for most standard indoor applications. However, their susceptibility to corrosion limits suitability for damp or humid environments.
Thermoplastic junction boxes provide superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties. PVC boxes resist moisture degradation effectively but may become brittle with UV exposure or extreme temperature fluctuations. Enhanced formulations incorporating UV stabilizers and impact modifiers offer improved performance in challenging environments.
Cast aluminum enclosures deliver exceptional durability and heat dissipation characteristics ideal for outdoor applications and locations with physical impact risks. Their excellent thermal conductivity makes them particularly suitable for applications involving power-dissipating components. Higher-grade marine-rated aluminum alloys offer superior salt-spray resistance for coastal installations.
Evaluating Box Configuration and Connection Options
Entry port configurations significantly influence installation flexibility and future adaptability. Professional-grade junction boxes typically feature multiple knockout options accommodating various conduit sizes. Concentric knockouts provide particularly valuable versatility when specific connection requirements may change during installation processes.
Internal mounting provisions represent essential features for applications requiring internal component installation. High-quality junction boxes incorporate bosses, standoffs, or mounting panels facilitating secure attachment of terminal blocks, relays, or control components. These features maintain proper clearances while ensuring stable mounting during operation.
Cover design significantly impacts maintenance accessibility and environmental protection. Hinged covers provide convenient access while preventing cover loss during service operations. Gasketed designs maintain environmental integrity when properly installed, while transparent covers facilitate visual inspection without compromising protection characteristics.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards and Installation Codes
Local code requirements often exceed national standards for specific applications. Municipal ordinances frequently impose additional installation requirements for particular occupancy types or installation locations. Consulting local authorities having jurisdiction (AHJs) regarding specific requirements represents a critical step in ensuring compliant installations.
Listing agency certifications provide essential verification of performance characteristics. UL/ETL listings indicate that products have undergone extensive testing verifying compliance with applicable safety standards. These certifications typically appear directly on products in the form of permanent markings or labels.
Installation location classification impacts permissible junction box types. NEC regulations differentiate between damp locations, wet locations, and hazardous environments—each requiring specific enclosure characteristics. Understanding these classification systems ensures selection of appropriate products for particular installation scenarios.
Installation Best Practices for Optimal Performance
Proper mounting techniques significantly influence long-term performance reliability. Junction boxes should attach securely to structural elements using appropriate fasteners sized for anticipated loads. Installation on unstable surfaces or using inadequate mounting provisions often leads to premature failure or regulatory non-compliance.
Sealing and weatherproofing procedures require careful attention, particularly for outdoor installations. Conduit entries should utilize appropriate fittings maintaining environmental ratings, while cover gaskets must compress properly to form effective seals. Drain provisions may be necessary for installations where condensation could accumulate.
Proper conductor organization within junction boxes represents a critical but often overlooked aspect of quality installations. Maintaining appropriate bend radii prevents insulation damage while facilitating future service access. Professional electricians typically group conductors logically (by circuit or function) while providing sufficient working space around connections.