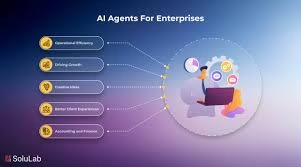
Artificial intelligence isn’t just a buzzword anymore. In enterprise environments, the shift from static AI tools to dynamic, autonomous systems is redefining how work gets done. AI agents for enterprises are a central part of this transformation. They blend advanced reasoning, automation, and contextual understanding to streamline business processes, cut operational costs, and elevate decision-making across departments.
This shift is more than incremental. According to recent research, many organizations are actively scaling agentic AI capabilities to real business functions, and this trend is expected to grow.
In this article, we’ll explore what AI agents are, how they operate, where they deliver the most value, and why enterprises that adopt them thoughtfully will gain a competitive edge.
What Are AI Agents for Enterprises?
At a basic level, an AI agent is a software system designed to act autonomously in an environment, make decisions, and execute tasks to achieve specific goals. They are different from traditional AI tools in that they don’t just respond to prompts or provide information. Instead, they interpret context, plan actions, interact with other systems, and carry out tasks end-to-end.
Unlike simple automation scripts or rules-based bots, AI agents can interact with data sources, analyze evolving conditions, and adjust behavior as situations change. This ability makes them uniquely suited to tackling complex enterprise workflows that require adaptability, endurance, and cross-system coordination.
How AI Agents Work
AI agents follow a cycle that combines perception, reasoning, and action:
- Perception: They gather data from internal systems, sensors, APIs, and user inputs. This could include anything from CRM records to real-time supply chain updates.
- Decision-Making: Using models and predefined goals, AI agents evaluate possible courses of action. They can weigh alternatives, anticipate outcomes, and select the most appropriate step.
- Action: Agents execute tasks, triggering workflows, updating systems, sending messages, or initiating processes across platforms.
This loop enables AI agents to operate independently once they are configured for a specific objective. Some advanced systems retain memory and context across multiple interactions, allowing them to manage multi-step workflows seamlessly.
Why Enterprises Are Turning to AI Agents
Organizations are increasingly adopting AI agents as they outgrow traditional automation. Here are the key drivers:
1. Complex Workflows Require Intelligent Automation
Many enterprise processes involve multiple systems, decision points, and exceptions. Human operators spend time switching between platforms, consolidating data, and monitoring outcomes. AI agents can shoulder much of this burden by orchestrating interactions across tools and handling routine exceptions, freeing humans to focus on higher-value work.
2. Decision Quality Improves with Intelligent Systems
AI agents don’t just execute predefined steps. They analyze data, incorporate patterns from past interactions, and adjust actions accordingly. This adaptive capability enhances decision quality, especially in dynamic contexts like supply chain management, financial forecasting, and customer engagement.
3. Operational Scale Without Proportional Cost
Scaling human labor to match business growth is expensive. AI agents, once deployed, can handle more workload without proportional increases in cost. They work around the clock, maintain consistency, and apply business rules uniformly—leading to better throughput with lower overhead.
4. Data-Driven Insights Enhance Strategic Planning
By integrating with analytics systems, AI agents can surface real-time insights and trends that inform strategic decision-making. Agents can highlight anomalies, recommend actions, or predict outcomes used by executives and operational leaders alike.
Key Enterprise Use Cases for AI Agents
AI agents shine in areas where tasks are complex, data-intensive, or highly repetitive. Here are some of the most impactful applications:
Customer Service Automation
AI agents can handle customer inquiries, route tickets to the right team, and even resolve common issues independently. These systems reduce response times, improve satisfaction, and lower support costs. Because agents handle routine interactions, human teams are available for complex or sensitive cases.
Sales and Marketing Orchestration
In sales, AI agents can automate lead qualification, track engagement signals across channels, and schedule follow-ups. Marketing teams benefit when agents monitor campaign performance, adjust targeting based on real-time data, and even personalize outreach at scale.
Finance and Risk Management
Finance teams use AI agents to automate invoice processing, detect fraud patterns, and evaluate risk scenarios. Agents can act on suspicious indicators faster than manual reviews, helping organizations protect assets and maintain compliance.
Supply Chain and Operations
Agents can monitor inventory levels, predict shortages, and recommend replenishment actions. By accessing multiple systems, ERP, logistics platforms, and forecasting tools, agents help enterprises respond quickly to disruptions and optimize resource planning.
IT Support and DevOps
AI agents manage routine IT tasks like password resets, system health checks, and software updates. In DevOps environments, they can oversee deployment pipelines, flag problematic build conditions, and even roll back changes when necessary, reducing downtime and manual intervention.
How AI Agents Improve Decision-Making
AI agents contribute to better decisions in several ways:
- Speed: Agents process data and respond in real time, enabling faster reactions to operational changes.
- Consistency: They apply rules uniformly, reducing subjective variance common in human decision-making.
- Context Awareness: Advanced agents retain state across sessions, giving them the ability to make contextually informed decisions.
- Predictive Insight: By integrating predictive models, agents can anticipate outcomes and recommend proactive actions.
This combination of analytical depth and operational capability positions AI agents not just as automation tools, but as decision support engines that integrate seamlessly into enterprise workflows.
Challenges in Adopting AI Agents
Despite their potential, AI agent deployment is not without challenges.
- Integration Complexity: Agents need access to multiple internal systems and real-time data streams. Ensuring seamless integration often requires significant engineering effort and robust API frameworks.
- Governance and Compliance: Autonomous decision-making introduces risks, particularly in regulated sectors. Clear governance policies, audit trails, and human-in-the-loop controls are essential to prevent unintended consequences.
- Organizational Readiness: Many enterprises struggle with change management. Successfully adopting AI agents often involves training teams, redefining roles, and aligning expectations with measurable business outcomes.
- Trust and Transparency: Users must trust agent decisions. Lack of visibility into how decisions are made can slow adoption. Effective design includes explainability features and clear interfaces for human supervision.
Best Practices for Deploying AI Agents
To realize the benefits of AI agents at scale, enterprises should follow these practices:
- Start with Clear Objectives: Define specific outcomes agents should achieve, whether it’s reducing response times, cutting costs, or boosting throughput. Clear goals help measure success.
- Ensure Data Quality and Access: Agents depend on reliable data. Establish unified data pipelines and robust access controls to ensure agents can work effectively across systems.
- Design for Transparency: Include mechanisms that explain how decisions are made. This builds trust and helps stakeholders understand agent recommendations.
- Implement Human-in-the-Loop Controls: Especially for high-impact decisions, maintain checkpoints where humans can validate or override agent actions. This balances autonomy with accountability.
- Monitor and Iterate: Track agent performance continuously. Use feedback loops to refine behavior, improve accuracy, and expand use cases over time.
Conclusion
AI agents for enterprises represent a fundamental shift in how business processes are executed. Moving beyond simple automation, agents integrate intelligence, execution, and adaptability, enabling organizations to streamline operations and improve decision-making at scale.
While challenges around integration, governance, and trust remain, clear adoption trends suggest that enterprises embracing this technology strategically will gain lasting advantages in efficiency and competitiveness.
As AI agents become standard components of enterprise software, they will bridge the gap between data insight and operational action, turning enterprise transformation from promise into reality.