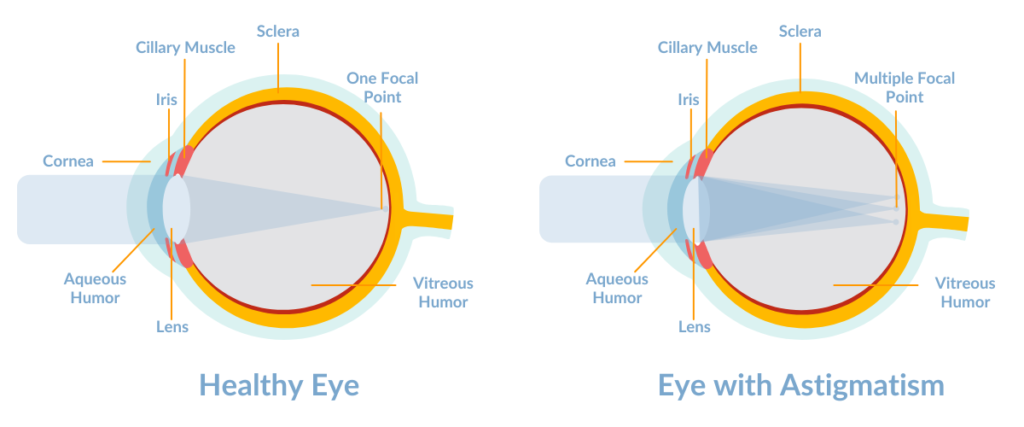
Astigmatism is a common vision condition that can cause blurred vision and challenges with tasks like reading or driving. Fortunately, it’s treatable with options like corrective lenses and advanced surgery. This blog covers astigmatism’s symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options to help you achieve clearer, healthier vision.
Understanding Astigmatism
What Is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens. Rather than being perfectly round, the cornea of someone with astigmatism is shaped more like a football, leading to distorted light refraction. This causes blurred or distorted vision for both near and far distances.
Unlike nearsightedness (myopia) or farsightedness (hyperopia), astigmatism affects vision equally in all directions. It can occur on its own or alongside other refractive errors, making it essential to properly diagnose and address the condition.
Common Symptoms of Astigmatism
The symptoms of astigmatism can vary from person to person but often include:
- Blurred or distorted vision (near and far).
- Eye strain or discomfort, especially after prolonged focus activities such as reading or screen time.
- Frequent headaches, often stemming from squinting or straining to see clearly.
- Difficulty seeing at night, particularly while driving.
- Double vision in some cases, especially if astigmatism is severe.
Left untreated, these symptoms can interfere with daily activities and impact your overall quality of life.
Diagnosis and Assessment
The Importance of Eye Exams
Routine eye exams are crucial for identifying and diagnosing astigmatism. Many people don’t realize they have the condition because it can develop gradually and may not always present with noticeable symptoms. Regular visits to an optometrist or ophthalmologist ensure that any changes to your vision are promptly addressed.
Tests for Astigmatism
Your eye care professional will conduct several tests to assess the degree and axis of astigmatism. These can include:
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures how well you can read letters on a chart at a specific distance.
- Keratometry: Determines the curvature of your cornea by measuring reflected light.
- Corneal Topography: Maps the surface of the cornea in detail to identify irregularities.
- Refraction Test: Uses various lenses to pinpoint the exact prescription needed to correct your vision.
These tests help create a tailored plan to manage and improve your sight effectively.
Corrective Measures
Glasses
One of the simplest and most common ways to correct astigmatism is through eyeglasses. Specially designed toric lenses are used to compensate for the irregular curvature of the cornea. Glasses are effective, affordable, and can be customized to suit your prescription and lifestyle. Plus, modern lens technology offers options like anti-glare coatings and lightweight materials for comfortable everyday wear.
Contact Lenses
For those who prefer a less visible corrective option, contact lenses are a popular choice. These come in several types:
- Soft Toric Lenses: Designed specifically for astigmatism, these lenses correct the irregular shape of your cornea.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses: Provide sharper vision by maintaining their shape on your eye, compensating for corneal irregularities.
- Hybrid Lenses: Combine the comfort of soft lenses with the clarity of RGP lenses.
- Specialty Lenses (e.g., scleral lenses): Ideal for severe or irregular astigmatism.
Contact lenses for astigmatism offer flexibility and are available for both daily and extended wear.
Refractive Surgery
For those seeking a more permanent solution, refractive surgery can correct astigmatism by reshaping the cornea. Popular options include:
- LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis): Uses a laser to reshape the cornea for precise focus, with options available at the cost of LASIK procedures like those in Utah.
- PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy): A similar laser procedure, ideal for thinner corneas.
- LASEK (Laser-Assisted Sub-Epithelial Keratectomy): Combines elements of LASIK and PRK for tailored solutions.
- Astigmatic Keratotomy (AK): Makes small incisions in the cornea to improve its shape.
Refractive surgery requires a candidacy evaluation, so consult your eye care professional to determine if you’re eligible.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
While corrective measures are the most effective way to address astigmatism, certain lifestyle adjustments can help reduce symptoms and maintain overall eye health.
Quick Tips for Managing Astigmatism
- Manage Screen Time: Follow the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) to reduce eye strain.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting while working, reading, or using screens.
- Stay Hydrated: Dry eyes can worsen symptoms. Eye drops or a humidifier can help if needed.
- Eye Exercises: Simple exercises like focusing on near and far objects can strengthen your eye muscles.
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in vitamins A, E, and C, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, to support eye health.
These strategies can enhance your comfort and help manage mild symptoms effectively.
Future Outlook
Astigmatism treatments are continuously evolving, with new advancements promising even more precise and comfortable solutions. Exciting developments include:
- Improved Laser Technology: Safer, faster, and more accurate refractive surgeries.
- Smart Contact Lenses: Currently in development, these may offer real-time vision correction and health monitoring.
- Early Detection Tools: Enhanced diagnostic devices for identifying astigmatism in its earliest stages.
Prioritizing regular eye exams and adopting healthy habits remain key to maintaining optimal vision, giving you the confidence to enjoy life fully.
Conclusion
Now that you have a better understanding of astigmatism, its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments, take control of your eye health by scheduling regular checkups with your eye care professional. Remember to address any vision changes promptly to prevent discomfort and maintain clear sight for years to come.