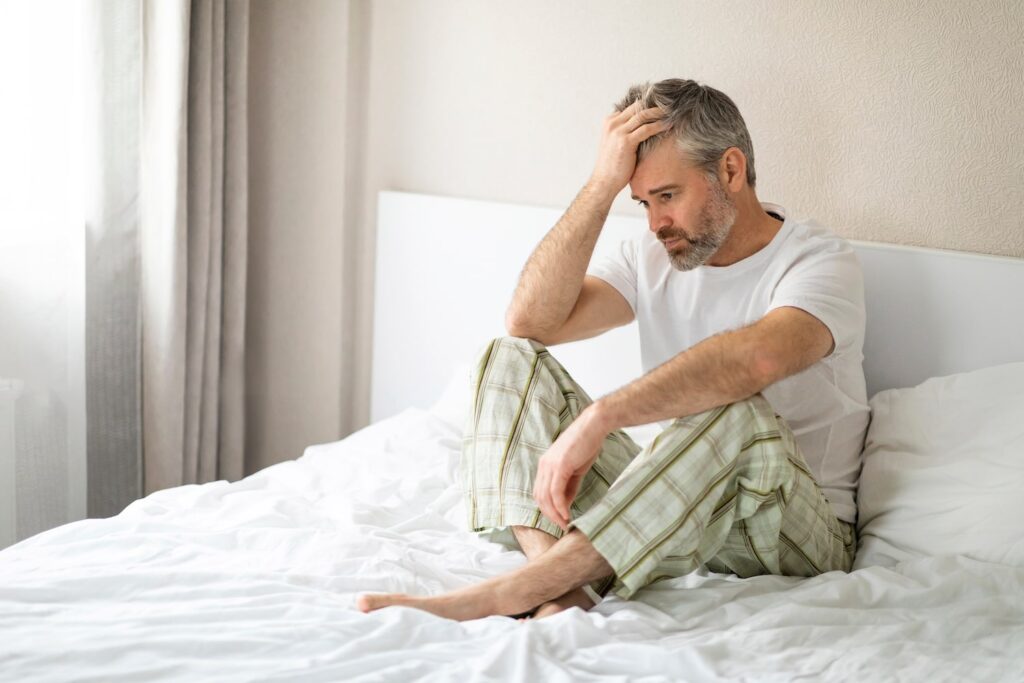
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a medical condition in which a man experiences ongoing difficulty achieving or maintaining a firm erection. While temporary changes in erectile response can occur due to fatigue, stress, or short-term illness, persistent erectile dysfunction often indicates an underlying health issue that deserves attention.
ED is a common condition and becomes more frequent with increasing age. However, it is not limited to older individuals. Lifestyle habits, chronic medical conditions, and emotional well-being all play important roles. Modern medical understanding shows that erectile dysfunction is often linked to overall physical health, especially heart and blood vessel function.
This article explains erectile dysfunction in clear, simple terms, outlines its most common causes, and reviews available treatment options in a medically responsible way.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
An erection occurs through a coordinated process involving blood circulation, nerve signals, hormones, and brain activity. When these systems work together properly, the body responds normally. When one or more of these systems is disrupted, erectile dysfunction may develop.
ED is not simply a local concern. In many cases, it reflects broader health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or hormonal imbalance. Because of this connection, erectile dysfunction is often viewed by healthcare professionals as an early indicator of systemic health problems.
Why Erectile Dysfunction Should Not Be Ignored
Many individuals assume erectile dysfunction is an unavoidable part of aging. While age can influence physical changes, persistent ED is not considered normal and should not be overlooked.
Medical research has shown that changes in erectile function may appear years before symptoms of heart disease or circulation problems. Early medical evaluation can help identify hidden conditions and allow timely treatment, improving long-term health outcomes.
Primary Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction usually results from multiple contributing factors rather than a single cause. These factors are commonly grouped into physical, hormonal, neurological, psychological, and lifestyle-related categories.
1. Circulatory and Blood Vessel Conditions
Healthy blood flow is essential for normal erectile response. Conditions that damage or narrow blood vessels are among the most frequent causes of ED, including:
● High blood pressure
● Heart disease
● Diabetes
● Elevated cholesterol levels
● Hardened or narrowed arteries
When blood flow is restricted, the body may not respond effectively.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones regulate many important body functions, including circulation and nerve activity. Erectile dysfunction may be associated with:
● Low testosterone levels
● Thyroid disorders
● Hormonal changes related to aging
● Chronic medical conditions affecting hormone production
Blood tests are often used to assess hormonal balance during diagnosis.
3. Nervous System Factors
The nervous system transmits signals that trigger physical responses. Erectile dysfunction can occur when nerve pathways are disrupted due to:
● Nerve damage from surgery or injury
● Neurological conditions
● Long-standing diabetes affecting nerve health
In these cases, specialized medical evaluation may be required.
4. Psychological and Emotional Health
Mental and emotional well-being significantly influence physical function. Psychological contributors to erectile dysfunction may include:
● Ongoing stress
● Anxiety
● Depression
● Performance-related concerns
Even when physical health is stable, emotional strain can interfere with normal body responses.
5. Lifestyle and Daily Habits
Certain lifestyle choices increase the risk of erectile dysfunction, such as:
● Smoking
● Excessive alcohol consumption
● Limited physical activity
● Obesity
● Poor sleep patterns
Addressing these factors often improves overall health and supports better treatment outcomes.
How Erectile Dysfunction Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis begins with a thorough medical discussion. A healthcare provider will review symptoms, medical history, and current medications. Additional steps may include:
● Physical examination
● Blood tests to check glucose, cholesterol, and hormone levels
● Blood pressure measurement
● Cardiovascular risk assessment
Accurate diagnosis helps identify the underlying cause and guides effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is highly manageable when treated under professional medical supervision. Treatment plans are individualized based on health status and contributing factors.
1. Oral Medications
Oral medications are commonly used to support erectile response by improving blood circulation. One such option is Cenforce 100, which contains Sildenafil Citrate. This medication works by relaxing blood vessels, allowing improved circulation when the body is stimulated.
When taken according to medical guidance, it has helped many individuals manage erectile dysfunction safely and effectively.
2. Sildenafil-Based Therapies
Several formulations containing Sildenafil Citrate are available. Cenforce is widely prescribed due to its established effectiveness and predictable action. These medications should always be used under professional supervision, especially by individuals with heart or blood pressure conditions.
Appropriate dosing and medical monitoring are essential for safety.
3. Lifestyle and Health Improvements
Healthcare providers often recommend lifestyle adjustments alongside medication, such as:
● Engaging in regular physical activity
● Following a balanced, heart-healthy diet
● Maintaining a healthy body weight
● Reducing alcohol intake
● Quitting tobacco use
● Managing stress effectively
These changes support vascular health and improve long-term results.
4. Psychological Support
When emotional or mental factors contribute to erectile dysfunction, counseling may be beneficial. Addressing anxiety, stress, or mood concerns can significantly improve treatment response and overall well-being.
5. Ongoing Medical Care
Long-term management of erectile dysfunction often includes follow-up appointments and monitoring, particularly when ED is linked to chronic conditions. Healthcare providers such as Woodstock Family Medicine offer comprehensive evaluations and personalized care plans focused on overall health management.
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction
Although erectile dysfunction cannot always be prevented, risk can be reduced by:
● Managing chronic health conditions
● Maintaining cardiovascular health
● Staying physically active
● Eating a balanced diet
● Avoiding tobacco use
● Seeking medical advice early
Preventive care plays an important role in maintaining long-term health.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Medical consultation is recommended if erectile dysfunction:
● Occurs frequently
● Persists over several months
● Causes emotional distress
● Appears alongside other health concerns
Early evaluation improves treatment success and helps identify potential underlying conditions.
Living Well With Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is a manageable medical condition and does not define overall health or quality of life. With accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and supportive lifestyle changes, many individuals experience significant improvement.
Open communication with healthcare providers and adherence to medical recommendations are key components of successful management.
Conclusion
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition often linked to broader health concerns. Understanding its causes and available treatment options empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward better health.
With professional medical care, evidence-based treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices, erectile dysfunction can be effectively managed, leading to improved overall well-being and long-term health outcomes.