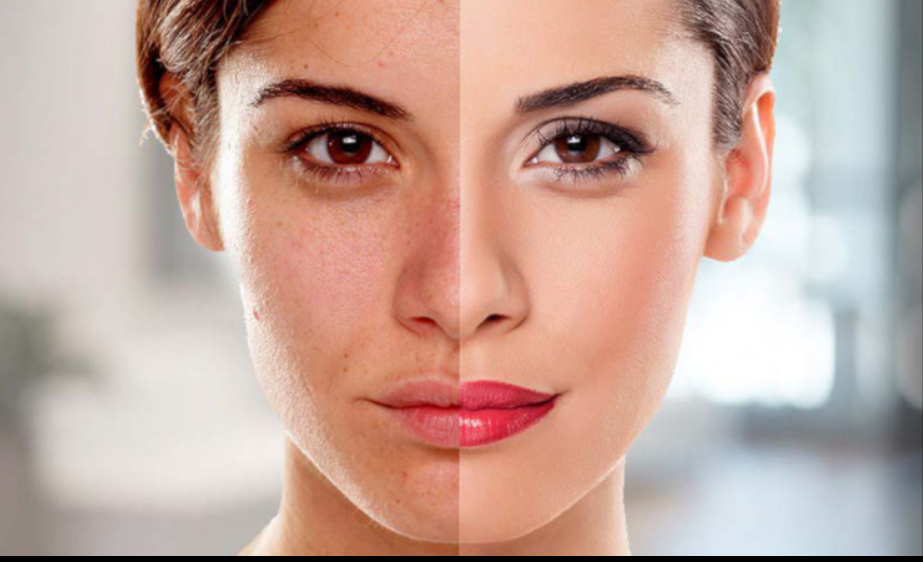
In the realm of skincare, achieving a radiant and even complexion is a common goal for many. Among the plethora of products available, Hydroquinone 4% Cream stands out as a potent option for skin lightening. However, it’s crucial to weigh its benefits and drawbacks against alternative solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the efficacy, safety, and considerations surrounding Hydroquinone 4% Cream compared to other skin-lightening options.
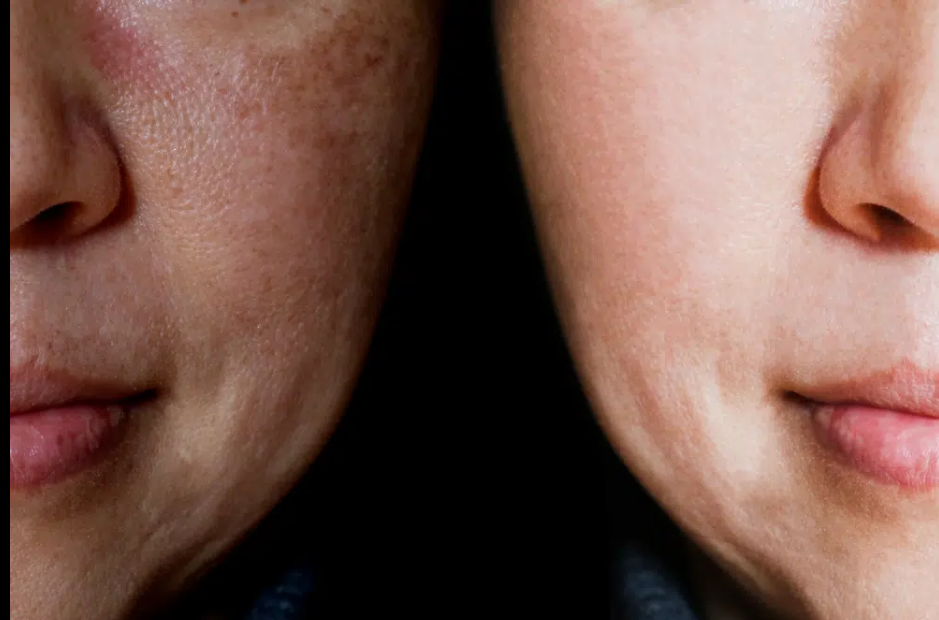
Understanding Hydroquinone 4% Cream
Hydroquinone 4% Cream is a topical agent renowned for its ability to lighten dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and melasma. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin in the skin, thereby reducing pigmentation and promoting a more uniform complexion. This cream is often recommended by dermatologists and skincare experts for its efficacy in treating various forms of discoloration.
Benefits of Hydroquinone 4% Cream
- Effective Lightening: Hydroquinone 4% Cream has demonstrated significant efficacy in fading dark spots and hyperpigmentation, leading to a brighter complexion.
- Targeted Treatment: Unlike some alternative solutions, Hydroquinone 4% Cream allows for precise application to specific areas of concern, ensuring targeted treatment.
- Dermatologist-Recommended: Many skincare professionals endorse the use of Hydroquinone 4% Cream for its proven results in addressing pigmentation issues.
Considerations and Potential Side Effects
While Hydroquinone Cream is widely regarded for its efficacy, it’s essential to acknowledge potential side effects and considerations associated with its use:
- Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience mild irritation, redness, or dryness when using Hydroquinone 4% Cream, particularly those with sensitive skin.
- Long-Term Use: Prolonged use of Hydroquinone 4% Cream has been linked to rare side effects such as ochronosis, a condition characterized by bluish-black pigmentation of the skin.
- Sun Sensitivity: Hydroquinone 4% Cream can increase skin sensitivity to sunlight, making it imperative to use sunscreen and practice sun protection habits diligently.
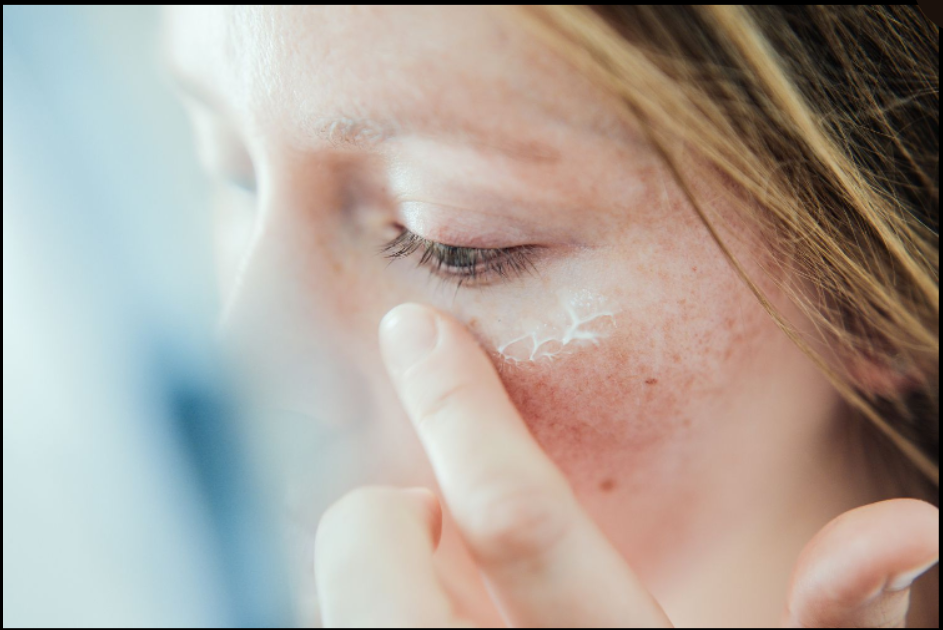

Exploring Alternatives to Hydroquinone 4% Cream
While Hydroquinone 4% Cream is a popular choice for skin lightening, several alternative options exist, each with its own set of benefits and considerations.
Vitamin C Serums
Vitamin C serums are revered for their antioxidant properties and ability to brighten the skin. These serums work by inhibiting melanin production and promoting collagen synthesis, resulting in a more luminous complexion. While not as potent as Hydroquinone 4% Cream, vitamin C serums offer a gentler approach to skin lightening, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or those seeking a more natural solution.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha arbutin is a natural skin-lightening ingredient derived from bearberry plants. It works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production, thereby reducing hyperpigmentation and promoting an even skin tone. Alpha arbutin is considered a milder alternative to Hydroquinone 4% Cream, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or those seeking a botanical-based solution.
Kojic Acid
Kojic acid is another popular ingredient in skin-lightening products, known for its ability to inhibit melanin production and reduce hyperpigmentation. Derived from fungi, kojic acid offers a natural alternative to Hydroquinone 4% Cream, albeit with slower results. While generally well-tolerated, kojic acid may cause irritation or sensitivity in some individuals, particularly those with sensitive skin.
1. Is Hydroquinone 4% Cream safe for all skin types?
- While Hydroquinone 4% Cream is generally considered safe for most skin types, individuals with hypersensitive skin or certain skin conditions may experience irritation or adverse reactions. It’s advisable to consult with a dermatologist before incorporating Hydroquinone 4% Cream into your skincare routine.
2. How long does it take to see results with Hydroquinone 4% Cream?
- Results may vary depending on individual skin type and the severity of pigmentation. Some users may notice improvements within a few weeks of consistent use, while others may require several months to achieve desired results. Patience and consistent application are key to maximizing the benefits of Hydroquinone 4% Cream.
3. Can Hydroquinone 4% Cream be used alongside other skincare products?
- Hydroquinone 4% Cream can be used in conjunction with other skincare products, but it’s essential to avoid combining it with certain ingredients that may increase skin sensitivity or counteract its effects. Consult with a dermatologist to ensure compatibility with your existing skincare routine.
4. Are there any precautions to consider when using Hydroquinone 4% Cream?
- Yes, it’s crucial to follow safety guidelines when using Hydroquinone 4% Cream. Avoid prolonged sun exposure and always use sunscreen with a high SPF to protect the skin from UV damage. Additionally, discontinue use if you experience severe irritation or adverse reactions, and consult with a dermatologist.
5. Can Hydroquinone 4% Cream be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals are generally advised to avoid using Hydroquinone 4% Cream due to potential risks to the developing fetus or infant. It’s best to consult with a healthcare professional before using any skincare products during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
6. Is Hydroquinone 4% Cream available over the counter or by prescription only?
- Hydroquinone 4% Cream is available in both over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription formulations. While lower concentrations (2% or less) may be available OTC, higher concentrations such as 4% typically require a prescription from a healthcare provider.
7. Can Hydroquinone 4% Cream be used to treat acne scars?
- While Hydroquinone 4% Cream may help fade post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) caused by acne, it’s not specifically formulated to treat acne scars. Dermatological procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy may be more effective for addressing acne scars.
8. Are there any alternatives to Hydroquinone 4% Cream for skin lightening?
- Yes, several alternatives to Hydroquinone 4% Cream exist, including vitamin C serums, alpha arbutin, kojic acid, licorice extract, and niacinamide. These ingredients offer gentler approaches to skin lightening and may be suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or those seeking botanical-based solutions.
9. Can Hydroquinone 4% Cream cause skin bleaching?
- Prolonged use of high concentrations of Hydroquinone, including 4% formulations, may potentially lead to skin bleaching or a condition known as ochronosis, characterized by bluish-black pigmentation. It’s essential to use Hydroquinone 4% Cream as directed and under the supervision of a dermatologist to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
10. How should Hydroquinone 4% Cream be incorporated into a skincare routine?
- Hydroquinone 4% Cream is typically applied to clean, dry skin once or twice daily, depending on the recommendation of a healthcare professional. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and application instructions carefully, avoiding contact with mucous membranes and sensitive areas of the skin.
Conclusion
In the quest for a brighter, more even complexion, Hydroquinone 4% Cream remains a formidable contender among skin lightening options. Its proven efficacy in treating hyperpigmentation and dark spots has solidified its status as a go-to solution for many individuals. However, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against potential side effects and consider alternative options, such as vitamin C serums, alpha arbutin, and kojic acid, which offer gentler approaches to skin lightening. Ultimately, consulting with a dermatologist or skincare professional can help determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual needs and preferences.







