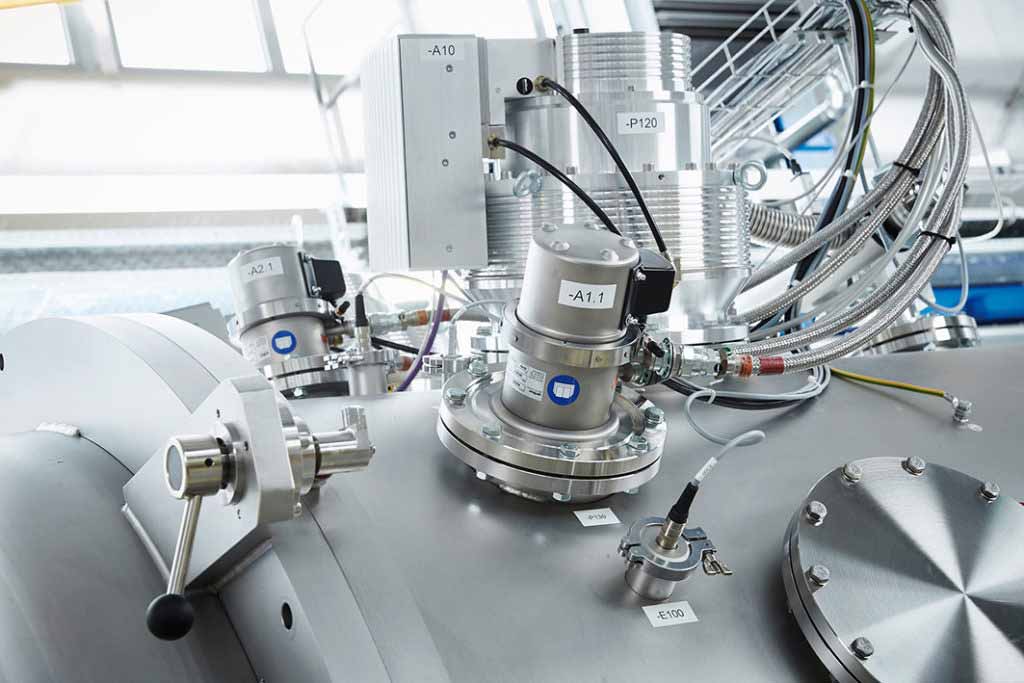
Vacuum pumps play a role in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to research and beyond. These versatile devices are designed to remove gas molecules from a sealed volume, creating a vacuum environment that is essential for various processes and applications. Let’s take a look at three common types of vacuum pumps, how they work, and their potential applications.
- Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps
- Functionality: Rotary vane vacuum pumps operate by using a series of vanes mounted on a rotor within a cylindrical housing. As the rotor spins, centrifugal force pushes the vanes outward, creating chambers between the vanes. As the chambers move past the inlet, gas is drawn in, and as they move towards the outlet, the gas is compressed and expelled. This continuous process creates a vacuum within the pump.
- Applications: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are widely used in applications where a medium to high vacuum level is required, such as vacuum packaging, freeze drying, degassing, and laboratory processes. They are valued for their reliability, relatively low cost, and ability to handle a wide range of gasses and vapors.
- Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps
- Functionality: Diaphragm vacuum pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm that moves up and down within a chamber to create suction and discharge cycles. As the diaphragm moves downward, it creates a vacuum within the chamber, drawing gas in through the inlet valve. When the diaphragm moves upward, the gas is compressed and expelled through the outlet valve. The sealed design of diaphragm pumps prevents oil contamination, making them ideal for cleanroom environments.
- Applications: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications that require oil-free and contamination-free vacuum, such as medical devices, analytical instruments, electronics manufacturing, and semiconductor processing. They’re also suitable for handling corrosive or aggressive gasses due to their chemically resistant materials.
- Scroll Vacuum Pumps
- Functionality: Scroll vacuum pumps consist of two interleaved spiral scrolls—one stationary and one rotating. As the rotating scroll orbits within the stationary scroll, the spiral paths gradually decrease in size, trapping and compressing gas molecules between them. This continuous compression process creates a vacuum within the pump.
- Applications: Scroll vacuum pumps are known for their quiet operation, low vibration, and oil-free design, making them well-suited for applications that require a clean and quiet vacuum source. They’re commonly used in laboratory research, analytical instrumentation, vacuum ovens, and semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Which Vacuum Pump Do You Need?
Vacuum pumps are indispensable devices that enable a wide range of industrial, scientific, and commercial processes. Understanding the different types of vacuum pumps, how they function, and their potential applications will help you select the right pump for a specific task or operation. Whether it’s creating a vacuum for packaging, analytical testing, or semiconductor fabrication, there’s a Chandler vacuum pump designed to meet the unique needs of every application.