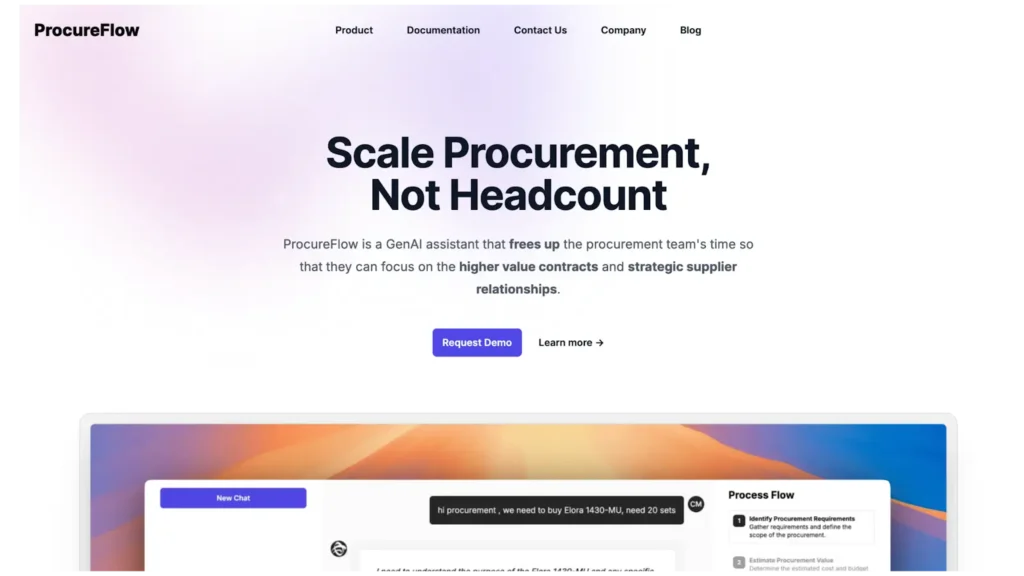
India’s retail sector is scaling at an unprecedented pace, placing pressure on store operations, customer service, and workforce efficiency.
According to a 2023 report by the Retailers Association of India (RAI), the Indian retail market is projected to reach over $190 trillion by 2034, driven by rapid store expansion and rising consumer expectations. As transaction volumes grow, retailers are increasingly exploring automation.
However, deploying best AI agents for retail requires careful integration to avoid disrupting store-level workflows that depend on speed, coordination, and human judgment.
Modern AI agents for retail are no longer limited to backend analytics; they now interact with inventory systems, customer queries, and operational support functions, making seamless adoption a strategic necessity rather than a technical choice.
Why Store-Level Workflows Are Sensitive to Disruption?
Retail store operations function on tight coordination between staff, systems, and customers. Any disruption at this level directly impacts sales, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
1. Stores operate in real time
Unlike centralized corporate functions, stores respond to live customer demand. AI systems that introduce delays, errors, or additional steps can slow checkout, replenishment, or service resolution, negatively affecting the in-store experience.
2. Staff rely on established routines
Store associates follow standardized workflows refined over time. Sudden changes driven by poorly integrated AI can create confusion, reduce efficiency, and increase resistance among frontline teams.
3. Multiple systems converge at the store level
Point-of-sale, inventory, staffing, and supplier systems intersect within stores. AI agents that fail to align with these systems risk fragmenting operations rather than streamlining them.
4. Customer interactions are context-heavy
Store-level decisions often depend on situational context, such as local demand or customer behavior. AI tools that ignore this context may generate recommendations that are impractical or irrelevant.
5. Operational errors scale quickly
A small workflow disruption replicated across hundreds of stores can escalate into widespread operational inefficiencies, making careful deployment essential.
Protecting store-level workflows is foundational to successful AI adoption in retail.
Identifying Retail Use Cases That Benefit From AI Without Friction
Not all retail processes require deep automation. Strategic use cases allow AI agents for retail to add value while preserving existing workflows.
1. Customer query handling outside peak hours
AI agents can manage routine customer inquiries after store hours, reducing staff burden without interfering with live in-store interactions.
2. Inventory visibility and alerts
Rather than automating ordering decisions, AI can surface low-stock alerts or demand anomalies, allowing store managers to act without losing control.
3. Workforce scheduling insights
AI-driven recommendations can support shift planning by analyzing demand patterns, while final decisions remain with store leadership.
4. Returns and policy guidance
AI agents can provide instant clarity on return eligibility and policies, reducing counter-level friction without changing approval authority.
5. Back-office task automation
Processes such as report generation or reconciliation can be automated without touching frontline store workflows.
Selecting low-friction use cases builds confidence and trust across store teams.
Designing AI Agents That Fit Existing Store Operations
Successful deployment depends on how well AI systems adapt to retail realities rather than forcing operational change.
1. Integration with current systems
AI agents must connect seamlessly with POS, inventory, and CRM platforms already in use. Parallel systems increase workload and undermine efficiency.
2. Minimal interface complexity
Store staff should not require extensive training to interact with AI tools. Simple dashboards and familiar workflows encourage adoption.
3. Configurable logic by store format
Different store sizes and formats operate differently. AI agents must allow configuration without code changes to reflect local operational needs.
4. Predictable behavior and responses
Consistency is critical in retail. AI agents should behave reliably across similar scenarios to avoid confusion or mistrust among staff.
5. Clear escalation pathways
When AI reaches its limits, seamless escalation to human teams ensures continuity and prevents operational dead ends.
Well-designed systems enhance operations without demanding behavioral change.
Maintaining Human Control While Using AI Agents at Scale
Retail remains a people-driven business. AI adoption must reinforce, not replace, human decision-making.
1. Human-in-the-loop approvals
For pricing, promotions, or stock adjustments, AI recommendations should require human validation, preserving accountability and local expertise.
2. Transparency in AI recommendations
Store managers need visibility into why AI suggests specific actions. Transparent logic increases trust and improves decision quality.
3. Override capabilities at the store level
Frontline leaders must retain the ability to override AI outputs based on situational awareness or local knowledge.
4. Continuous staff feedback
Feedback from store teams helps refine AI behavior and prevents misalignment between system design and operational reality.
5. Clear ownership and accountability
Defined roles ensure clarity on who is responsible for decisions influenced by AI, reducing internal friction and audit risk.
Human oversight ensures AI supports retail teams rather than displacing them.
Evaluating the Best AI Agents for Retail Environments
Choosing the best AI agents for retail requires evaluation beyond feature lists or pilot performance.
1. Retail-specific operational alignment
General-purpose AI tools often fail in store environments. Retail-focused agents are built around transaction volume, seasonality, and frontline workflows.
2. Scalability across locations
AI agents must perform consistently across multiple stores without increasing complexity or management overhead.
3. Low-latency performance
Retail operations cannot tolerate delays. Response times must meet the demands of fast-moving customer interactions.
4. Governance and compliance readiness
Data handling, access controls, and audit logs must align with enterprise and regulatory requirements.
5. Long-term adaptability
Retail strategies evolve rapidly. AI agents should support continuous improvement without disruptive redeployment cycles.
Strong evaluation criteria prevent costly missteps at scale.
Change Management as a Critical Success Factor
Technology alone does not ensure successful adoption. Structured change management protects store-level stability.
1. Gradual rollout strategies
Piloting AI in limited store clusters allows refinement before enterprise-wide deployment.
2. Store-first communication
Clear communication about AI’s role reduces fear and resistance among frontline staff.
3. Training focused on enablement
Training should emphasize how AI simplifies work rather than how it replaces roles.
4. Measuring operational impact holistically
Success metrics should include staff efficiency, customer satisfaction, and error reduction, not just cost savings.
5. Continuous optimization cycles
Regular reviews ensure AI systems evolve alongside store operations rather than becoming misaligned over time.
Effective change management anchors AI adoption in operational reality.
Conclusion
Retailers in India face mounting pressure to scale operations without compromising store-level efficiency. AI adoption offers clear advantages, but only when implemented with sensitivity to frontline workflows.
By selecting appropriate use cases, designing systems that integrate seamlessly, and maintaining human oversight, retailers can deploy AI agents for retail without operational disruption.
Evaluating the best AI agents for retail now requires a focus on reliability, adaptability, and governance rather than automation speed alone.
Organizations that adopt AI platforms designed for real-world retail environments demonstrate how intelligent agents can enhance productivity while preserving the human-centric nature of store operations.