Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) molding is a fast-growing manufacturing method used to produce flexible, durable, and high-performance rubber parts. With wide use across industries such as medical, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, LSR molding offers reliability and precision for producing both simple and complex components.
What Is LSR Molding?
LSR molding, short for Liquid Silicone Rubber injection molding, is a manufacturing process that involves injecting a two-part liquid silicone compound into a heated mold. Once cured, the result is a flexible, high-strength rubber product with excellent chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties.
How Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Works
The LSR molding process follows a cycle that ensures consistent, high-volume part production with minimal material waste. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved:
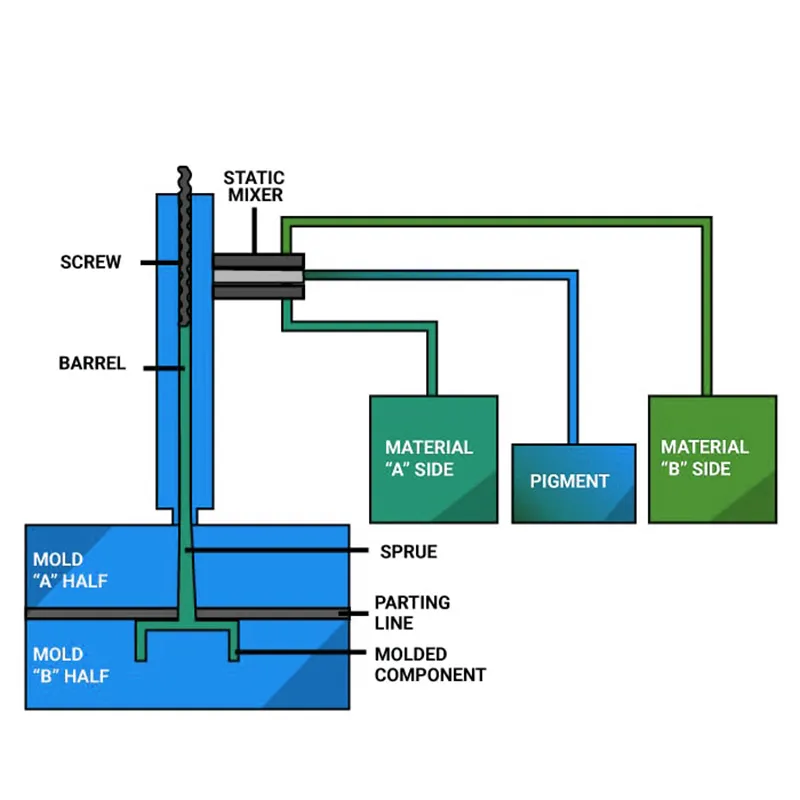
1. Material Preparation
LSR is made from two liquid components (Part A and Part B), which are mixed at a 1:1 ratio. Additives such as color pigments or curing agents may also be included.
2. Injection Into Mold
The mixed silicone is injected into a closed, heated mold under high pressure. LSR’s low viscosity allows it to flow easily into intricate mold cavities.
3. Curing Process
The material cures rapidly inside the mold due to the heat, transforming the liquid silicone into solid rubber. This step is highly controlled for precise part formation.
4. Part Ejection and Cooling
Once the part is cured, it is ejected from the mold and allowed to cool. Automated systems often handle this step in high-volume operations.
Key Properties of Liquid Silicone Rubber
Liquid Silicone Rubber exhibits a unique combination of characteristics that make it suitable for a wide range of products:
- High heat resistance (up to 200°C and beyond)
- Excellent flexibility and elasticity
- Biocompatibility and hypoallergenic qualities
- Resistance to UV, ozone, and chemicals
- Electrical insulation properties
Advantages of LSR Molding
Businesses across many sectors choose LSR molding for specific benefits that alternative materials and processes can’t offer.
Precision and Repeatability
LSR injection molding ensures consistent dimensions, surface quality, and part integrity — ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances.
Automation-Friendly
The fully automated process reduces labor costs and production times, improving efficiency in mass production.
Safe for Medical and Food Use
Due to its biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes, LSR is widely used for medical devices, baby products, and kitchenware.
Complex Geometries Possible
Because LSR flows easily into small cavities, it’s possible to produce parts with intricate shapes and undercuts without secondary processing.
Industries That Use LSR Molding
Automotive
In the automotive sector, LSR components are used for gaskets, seals, sensors, connectors, and lighting due to their ability to withstand heat and vibrations.
Medical and Healthcare
Liquid silicone rubber is commonly used in catheters, respiratory masks, baby bottle nipples, and implantable devices.
Consumer Goods
Wearable tech, kitchen utensils, and baby care items benefit from LSR’s comfort, flexibility, and safety.
Electronics
LSR’s electrical insulation properties make it suitable for components such as LED lenses, keypads, and housing for sensors.
Common Products Made with LSR Molding
- Sealing gaskets
- Diaphragms
- Valves
- Baby pacifiers
- Electrical connectors
- O-rings
- Wearable wristbands
These products often require durability, flexibility, and heat resistance — all hallmarks of silicone rubber.
Designing for LSR Injection Molding
When designing parts for LSR molding, consider the following guidelines to ensure optimal results:
Wall Thickness
Keep wall thickness uniform where possible. Thin walls should be no less than 0.5 mm, and thicker sections may require venting to avoid air traps.
Undercuts and Complex Shapes
LSR can fill detailed and undercut areas, but mold design must allow for part ejection without tearing.
Surface Finish
Tooling should be polished or textured according to the desired finish. LSR replicates mold surfaces accurately.
Draft Angles
Unlike thermoplastics, LSR does not always need draft angles for demolding, but adding slight angles can help in automatic ejection.
Tooling Considerations for LSR Molding
Tooling for LSR molding must handle high temperatures and frequent cycling. Materials like hardened steel or aluminum with appropriate thermal control systems are commonly used.
Key tooling features include:
- Heated cavities (typically 160°C to 220°C)
- Cold-runner systems to prevent material waste
- Vacuum venting to eliminate air bubbles
- Automatic part removal features
Future of LSR Injection Molding
As industries demand higher performance materials and faster manufacturing cycles, LSR molding continues to evolve. Innovations like multi-shot molding, automated degating, and advanced mold flow simulation are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Sustainable and bio-based LSR formulations are also emerging, making this technology more environmentally friendly without sacrificing performance.
Final Thoughts
LSR molding is a powerful method for producing flexible, durable, and precision parts across a range of industries. With fast cycle times, low waste, and design freedom, it continues to be a top choice for manufacturers seeking quality and efficiency.
By understanding the process, applications, and design best practices, companies can unlock the full potential of liquid silicone rubber injection molding for their next project.