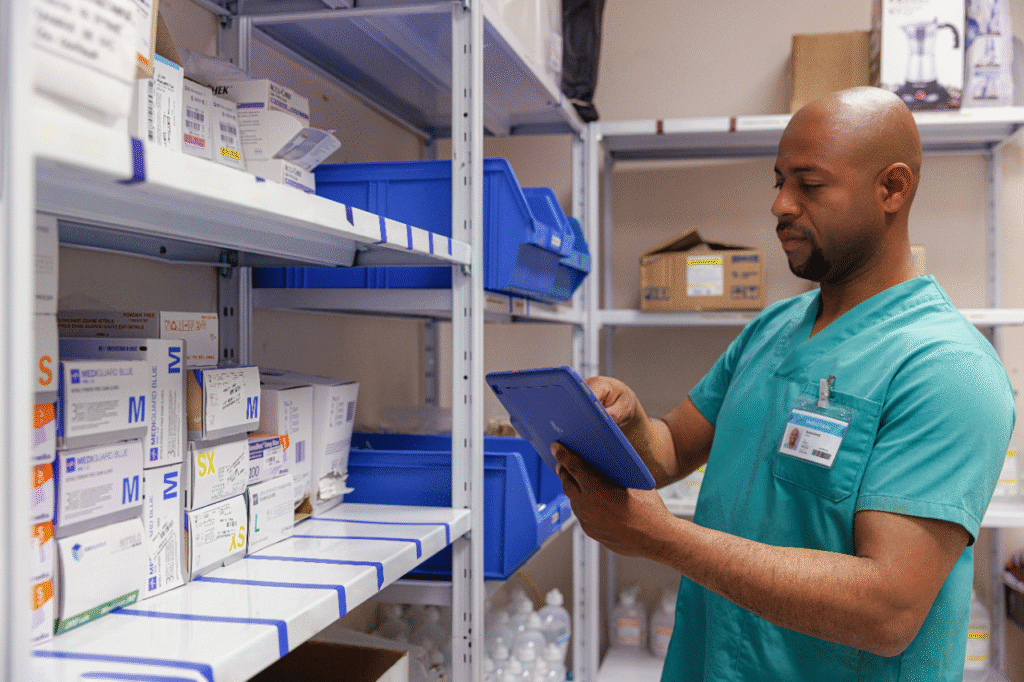
Hospitals are complex environments, constantly moving and managing a vast amount of equipment and patients. With so many things happening at once, it can be tough to keep track of everything. This is where RFID-based tracking systems come in. These systems use radio waves to automatically track both medical equipment and patient movement, making hospital operations more efficient and improving the quality of care.
Let’s break down how RFID works, how it’s used in hospitals, and the benefits it brings to the table.
What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that allows objects (like medical devices or patient wristbands) to be identified and tracked using radio waves. The system consists of three main parts:
- RFID Tags: These are small devices that hold data and are attached to items (e.g., equipment or patient wristbands). Tags come in two main types:
- Passive tags: They don’t have a battery and rely on the RFID reader to power them.
- Active tags: These have batteries and can transmit data over longer distances.
- Passive tags: They don’t have a battery and rely on the RFID reader to power them.
- RFID Readers: These are devices that send out radio waves to read the tags. They can be fixed in place (like at doorways or in hallways) or handheld for mobile scanning.
- Middleware/Software: The data gathered by the readers gets sent to a central system that processes the information and provides real-time updates on location, status, or other relevant details.
Tracking Medical Equipment
Hospitals have tons of valuable equipment — everything from ventilators to portable X-ray machines. This equipment is constantly in use, moved around from room to room, and sometimes hard to find when it’s needed most. RFID helps solve this problem by allowing hospitals to track these items in real-time.
How it Works:
- Tagging Equipment: Each piece of equipment gets a small RFID tag attached to it. For more expensive or mobile items, hospitals often use active tags, as they provide longer-range tracking and don’t require a reader to be nearby to capture the signal.
- Reader Placement: Fixed RFID readers are set up at key locations like department entrances or storage areas. Every time tagged equipment passes by one of these readers, its location is recorded.
- Real-Time Tracking: This data feeds into a system that provides hospital staff with live updates on where the equipment is located. Some systems even send out alerts if an item is taken from its designated area.
Benefits for Equipment Tracking:
- Faster Access: With real-time location data, staff can find equipment quickly, saving valuable time, especially in emergencies.
- Better Utilization: RFID shows exactly how often each piece of equipment is used, so hospitals can manage their inventory more effectively, avoiding over-purchasing.
- Maintenance: Knowing where equipment is and how often it’s used helps with scheduling maintenance, ensuring devices are always in working order.
- Reduced Losses: With tracking data, it’s harder for equipment to be misplaced or stolen, as alerts can be sent when things go missing.
Tracking Patient Movement
Hospitals aren’t just tracking equipment. RFID is also being used to monitor patients as they move through the facility. From the moment a patient arrives at the hospital until they are discharged, RFID can ensure they’re in the right place at the right time.
How it Works:
- Patient Wristbands: When a patient arrives, they’re given an RFID wristband that holds their identification data. This wristband works just like a barcode but is much more efficient.
- Location Updates: As patients move through the hospital — whether they’re going for a test, in surgery, or being moved from one room to another — the RFID readers capture their location whenever they pass by. This helps keep track of where they are at any given moment.
- Integration with Hospital Systems: The RFID system integrates with the hospital’s Electronic Health Records (EHR), which means the system automatically logs when the patient arrives at a certain location or receives a treatment. This can also help update medical staff on the patient’s status in real-time.
Benefits for Patient Tracking:
- Improved Safety: RFID ensures the right patient is receiving the right care. This helps prevent errors like incorrect medication administration or mix-ups during surgery.
- Better Flow: RFID helps hospital staff identify bottlenecks in patient movement. If a patient is waiting too long for a procedure, staff can see this in real-time and adjust accordingly.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: With RFID, family members can be updated on a patient’s progress or location, reducing anxiety and improving communication.
- Emergency Situations: In critical care situations, knowing the exact location of each patient allows staff to respond quickly and accurately.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Of course, when dealing with sensitive patient data, security is a top priority. RFID systems in hospitals must comply with regulations like HIPAA (in the U.S.) to ensure patient information is protected. The RFID tags themselves don’t carry personal health information, but they link to a central system that does. Therefore, hospitals need to implement strong encryption and access controls to keep this data secure.
There are also privacy concerns around being tracked constantly. Some patients might feel uneasy about being monitored, even if it’s for their own safety. Hospitals need to make sure patients are informed about how RFID is being used and the benefits it provides.
Challenges to Implementation
While RFID systems can transform hospital operations, they’re not without challenges:
- Cost: The initial setup, including purchasing tags, readers, and integrating the system, can be expensive, particularly for larger hospitals.
- Interference: Hospitals are filled with equipment and materials (like metal objects) that can sometimes interfere with RFID signals, leading to tracking errors.
- Durability of Tags: RFID tags must withstand harsh conditions like sterilization in hospital settings, which can limit the types of tags that are used.
- Staff Training: For RFID to be effective, staff need to be trained to use the system properly and understand its benefits.
The Future of RFID in Healthcare
The potential for RFID in healthcare is enormous. As hospitals adopt more advanced technologies like IoT sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and wearable health devices, RFID will play a key role in making healthcare systems smarter. It’s not just about tracking equipment and patients, but also improving predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and even personalized patient care.
In the coming years, RFID will continue to evolve, helping hospitals become more efficient, reduce costs, and ultimately provide better care to patients.
In summary, RFID is a game-changer for hospital management. By allowing real-time tracking of both medical equipment and patient movement, RFID systems improve efficiency, safety, and patient outcomes. As hospitals continue to implement these technologies, we can expect even greater advancements in patient care and hospital operations. Find out more at https://www.idplate.com/rfid-tags/