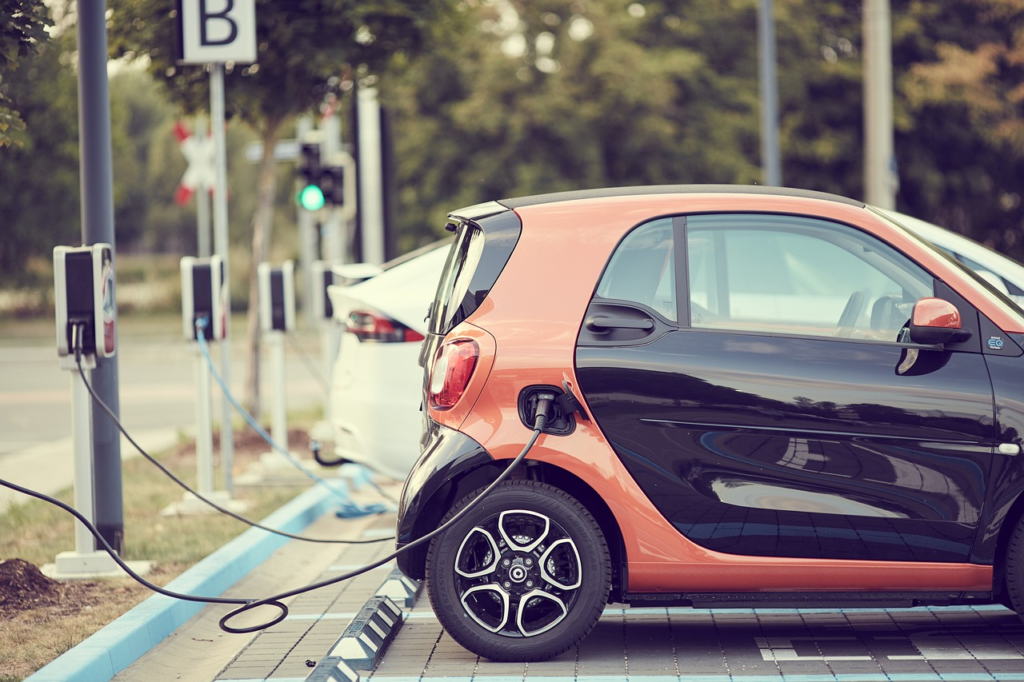
As the world shifts towards sustainable energy, understanding electric vehicle (EV) chargers is more important than ever. In this guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about EV chargers, from different types and their functionalities to installation tips and charging etiquette. Get ready to enhance your journey into the electric vehicle landscape and make informed decisions for your driving experience.
Installation and Compatibility
Installing an EV charger involves several key considerations to ensure compatibility and efficiency. It’s best to find an EV charger manufacturer that creates devices meant for your specific car model. First, it’s essential to assess the type of charger needed — Level 1 or Level 2 — based on your vehicle’s requirements and your driving habits. A Level 1 charger typically plugs into a standard outlet, making installation straightforward, while a Level 2 charger requires a dedicated circuit and may necessitate professional installation.
Next, consider the location of the EV Charger. It should be easily accessible to the vehicle and installed in an area with an adequate electrical supply. Compatibility with your EV is crucial; check the vehicle’s specifications and connector type to ensure a seamless charging experience. Finally, keep in mind local regulations, as they may dictate specific installation practices and safety standards. Proper planning will facilitate a successful installation, maximizing the convenience of your electric vehicle.
Charging Speeds and Power Ratings
Charging speeds for EV chargers are primarily determined by their power ratings, which are measured in kilowatts (kW). Level 1 chargers, typically rated at 1.4 kW, provide a slow charging option, offering about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging.
Level 2 chargers, commonly rated between 3.7 kW and 22 kW, significantly improve charging speed, delivering 10 to 60 miles of range per hour depending on the vehicle and charger characteristics. DC Fast Chargers, rated from 50 kW to over 350 kW, allow for rapid charging, providing 100 miles of range in approximately 30 minutes. Selecting the right charging speed ensures that drivers can efficiently power their vehicles based on their usage patterns and lifestyle needs.
Types of EV Chargers
There are also different types of EV chargers you should be aware of because they each serve a different purpose. Here are your options:
- Level 1 chargers
- Level 2 chargers
- DC fast chargers
- Tesla superchargers
- CHAdeMO Chargers
- CCS (Combined Charging System)
Each is designed for specific charging needs. Level 1 chargers are ideal for home use, providing slow charging through standard outlets. Level 2 chargers are faster and more suitable for residential and commercial locations. DC fast chargers offer rapid charging for long journeys, while Tesla superchargers are specifically for Tesla vehicles. For a deeper dive into how these charging types apply to specific vehicles, particularly in light of evolving tech like the Tesla Cybertruck, check out the Tesla Cybertruck EV Charging Discussion. On the other hand, CHAdeMO and CCS connectors cater to various manufacturers, enhancing versatility for EV owners.
Connection Types
Connection types affect compatibility with different electric vehicles. The two most common types are Type 1 and Type 2 connectors. Type 1, also known as J1772, is predominantly used in North American vehicles and supports Level 1 and Level 2 charging.
Conversely, Type 2 connectors are standard in Europe, accommodating both home and public charging stations. Additionally, connectors such as CHAdeMO and CCS (Combined Charging System) are essential for fast charging; CHAdeMO is popular among manufacturers like Nissan, while CCS is increasingly adopted by a variety of brands, including Ford and Volkswagen. Selecting the right connection type ensures effective energy transfer and compatibility with EVs.
Home Vs. Public Charging
Home charging refers to the convenience of charging your electric vehicle (EV) at your residence, typically using a Level 1 or Level 2 charger. This option is often more convenient, allowing drivers to plug in overnight and wake up to a fully charged vehicle, integrating seamlessly into daily routines.
On the other hand, public charging stations are found in various locations, such as shopping centers, highways, and parking lots, catering to drivers on the go. Public chargers usually include Level 2 and DC fast chargers, enabling quicker recharges during long trips or when away from home. While public charging is essential for flexibility, home charging provides unmatched convenience for everyday use, making it integral to the EV ownership experience.
Charging Costs
Charging costs for electric vehicles (EVs) vary based on several factors, including energy rates and charger types. Home charging typically uses residential electricity rates, which can range from $0.10 to $0.30 per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
For instance, charging an EV might cost around $5 to $15 for a full charge, depending on its battery capacity. Public charging stations may charge by the minute or kWh and can be more expensive, particularly for DC fast charging. Some locations may offer free charging or membership-based pricing. By understanding these costs, EV owners can better manage their expenses and select optimal charging options that suit their driving habits.
In conclusion, understanding EV chargers empowers you to make informed decisions about your electric vehicle ownership. By considering factors such as type, installation, charging speeds, and costs, you can enhance your driving experience and maximize convenience. Embrace the transition to sustainable energy with confidence, knowing that the right charger aligns with your lifestyle and driving needs.