Introduction
Workplace security is changing quickly because of new technology and the need for organizations to protect their spaces. Employee identification systems are a key part of this change, improving security measures and making sure only authorized people can enter sensitive areas.
Here are some key trends that are shaping the future of workplace security:
- ID Badges: These are essential for controlling access, as they provide visual identification and tracking capabilities.
- Biometric Methods: These methods offer higher accuracy and convenience through fingerprint or facial recognition technology.
- AI Integration: This integration is transforming surveillance by enabling real-time threat detection.
As businesses adapt to these changes, it’s important to understand their impact in order to maintain a secure work environment.
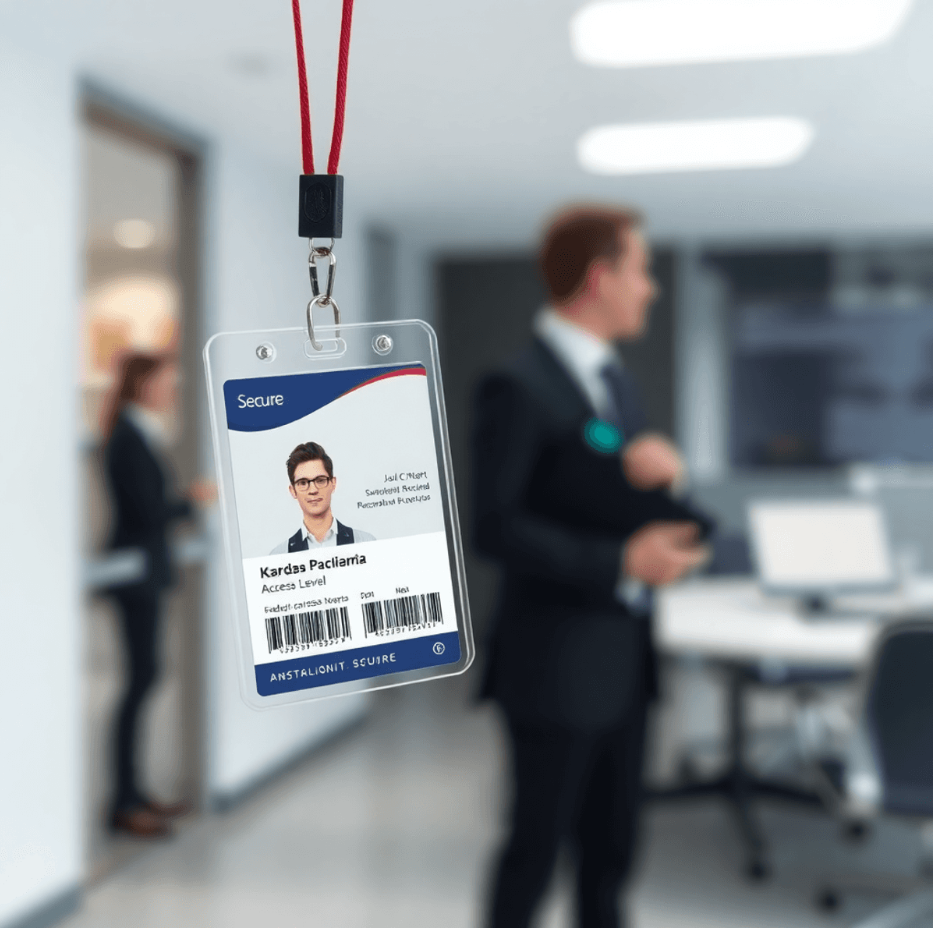
1. The Role of ID Badges in Modern Workplace Security
Custom Printed ID badges are an essential part of modern access control systems. They act as the first line of defense against unauthorized entry into workplaces. These badges not only provide access to certain areas but also assist organizations in keeping their facilities secure and well-organized.
Key functions of ID badges include:
- Regulating Access: By implementing a system where each badge corresponds to predefined access rights, businesses can effectively manage who enters their premises and restrict entry to sensitive areas.
- Deterring Unauthorized Individuals: Visible identification acts as a deterrent, discouraging potential intruders from attempting unauthorized access due to the obvious identification requirement.
- Facilitating Quick Identification: In emergency situations, ID badges allow for rapid identification of personnel, ensuring that first responders can quickly ascertain who is present within the premises.
The security features built into employee ID badges play a significant role in creating a safer workplace. They also promote a culture of accountability and trust among employees. As security technologies continue to evolve, ID badges will remain crucial in upholding workplace safety protocols and improving overall organizational security measures.
2. Biometric Technologies: The Future of Employee Authentication
Biometric technology has emerged as a leading method for employee authentication, with companies offering enhanced accuracy and convenience compared to traditional techniques such as PINs or passwords. You can visit the website for more information on how biometric security solutions can enhance data protection. Various methods are being adopted by organizations, including:
- Fingerprint scanning: A widely recognized form of biometric authentication that utilizes unique fingerprint patterns for secure access.
- Facial recognition systems: Employing advanced algorithms to identify individuals by analyzing facial features, providing a quick and efficient means of verification.
These biometric systems streamline the authentication process while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Unlike passwords, which can be forgotten or stolen, biometric traits are inherently unique to each individual.
However, the adoption of biometric technologies does present potential security concerns. The storage and management of biometric data require stringent measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Implementing robust encryption protocols is crucial to safeguarding this sensitive information. Organizations must prioritize security measures that ensure biometric data is securely stored and transmitted, thereby maintaining employee trust and compliance with regulatory standards.
The integration of these advanced authentication methods signifies a shift towards more secure workplace environments, aligning with the growing demand for reliable identification solutions.
3. AI-Powered Surveillance: Enhancing Security Monitoring Capabilities
Artificial intelligence is shaping the future of workplace security through innovative surveillance practices. By integrating advanced video analytics, organizations can implement real-time threat detection and response mechanisms. Key features include:
- Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms analyze video feeds for unusual activity, enabling immediate alerts to security personnel when anomalies are detected.
- Facial Recognition Technology: AI systems can identify individuals based on stored images, streamlining access control and monitoring.
Despite the benefits, organizations face significant challenges with AI in security systems:
- Privacy Invasion: As surveillance technology becomes more widespread, there is a growing concern about invading privacy. Employees may feel uncomfortable being constantly monitored, raising ethical questions about consent and transparency.
- Algorithmic Bias: If not carefully managed, AI systems could misidentify individuals or disproportionately target specific groups based on flawed data sets. This poses risks to fairness and equality in security practices.
Navigating these challenges requires a balanced approach that combines cutting-edge technology with ethical considerations, ensuring a secure yet respectful workplace environment.
4. Blockchain Technology: Securing Identity Verification Processes
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized framework that enhances the integrity and authenticity of employee identities. This innovative approach significantly reduces the risks associated with fraud and impersonation attempts, providing organizations with a robust method for identity verification purposes.
Key benefits of blockchain in workplace security include:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases, blockchain operates on a distributed ledger, making it nearly impossible for a single entity to manipulate identity data.
- Immutability: Once information is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures that access logs remain tamper-proof, providing an accurate historical record of employee entries and exits.
- Enhanced Privacy: Employees can control their identity information, sharing only what is necessary for verification while keeping sensitive data secure.
Specific use cases illustrate blockchain’s potential in workplace environments:
- Secure Access Logs: Organizations can utilize blockchain to maintain a transparent and unalterable record of employee access, enhancing accountability.
- Digital Certificates: Employers can issue tamper-proof digital certificates for authentication purposes, mitigating the risk of fraudulent claims about credentials or identities.
As businesses strive to bolster their security frameworks, integrating blockchain technology presents an effective strategy for safeguarding employee identification processes.
5. Smart ID Cards: Balancing Security with Convenience
Organizations are increasingly upgrading from traditional plastic IDs to smart ID cards incorporating RFID chips. These advanced solutions provide enhanced security features and user-friendly functionalities. Key benefits include:
- Encrypted Data Storage: Smart ID cards protect sensitive information through encryption, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Contactless Scanning: Employees can gain entry quickly without the need for physical contact, streamlining the access process and improving convenience.
Despite these advantages, there are potential drawbacks associated with smart card technology:
- Compatibility Issues: Organizations may face challenges integrating smart ID systems with existing infrastructure or other security technologies.
- Reliance on External Power Sources: Some smart cards require batteries or external charging, which can present operational challenges if not managed properly.
As businesses navigate these factors, finding the right balance between enhanced security and convenience remains a priority in the evolving workplace landscape. The adoption of smart ID solutions reflects a commitment to leveraging technology for improved identification processes while addressing potential limitations effectively.
How businesses are upgrading from traditional ID cards to smart, encrypted ID solutions
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need for advanced security measures in their employee identification systems. Upgrading from traditional plastic IDs to smart ID badges for employees offers numerous benefits:
1. Enhanced Security Features
Smart IDs typically include encrypted data storage, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access or replicate credentials.
2. Contactless Functionality
Many smart ID cards support NFC (Near Field Communication) technology, allowing for quick and efficient access through simple scanning. This not only speeds up entry but also reduces physical contact, a vital consideration in today’s health-conscious workplaces.
3. Integration with Other Systems
Smart ID solutions can integrate seamlessly with existing security infrastructures, such as access control systems and surveillance technologies. This creates a cohesive security environment that enhances overall protection.
However, organizations must navigate certain challenges when implementing smart ID solutions:
- Compatibility Issues: Some legacy systems may not support the latest technology, necessitating further investment in upgrades.
- Reliance on External Power Sources: Certain smart IDs may require battery power or charging, which can complicate usage in environments where constant availability is crucial.
The shift towards smart and encrypted identification methods reflects a growing commitment to workplace security and efficiency.
6. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthening Access Control Measures Beyond IDs Alone
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods in conjunction with employee ID systems enhances security by adding additional layers of protection against unauthorized access. Relying solely on ID badges can expose organizations to risks, especially if these physical identifiers are lost or compromised. By integrating MFA, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches.
Commonly used MFA technologies include:
- Mobile Authenticator Apps: These applications generate time-sensitive codes that users must enter alongside their ID badges. Examples include Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator.
- Biometric Verification Methods: Fingerprint scanners or facial recognition technologies can be employed to validate identity further, ensuring that only authorized personnel gain access.
The combination of these technologies creates a robust security framework. Organizations may also explore integrating MFA solutions with existing employee identification frameworks for seamless user experiences. This integration not only fortifies access control measures but also aligns with the evolving landscape of workplace security, emphasizing the need for comprehensive protection strategies as highlighted in The Future of Workplace Security: Trends in Employee Identification Technology.
7. Staying Ahead in ID Security Trends: Practical Steps for Businesses to Take Today
Organizations must adopt proactive measures for effective ID security management. Here are actionable recommendations:
- Conduct Regular Audits: Evaluate system vulnerabilities frequently to identify and address weaknesses in employee identification technologies.
- Foster Cybersecurity Awareness: Implement training programs that educate employees about security protocols, phishing attacks, and the importance of safeguarding their identification credentials.
- Stay Informed on Trends: Keep abreast of emerging technologies in workplace security, ensuring that the organization can adapt to new advancements in employee identification systems.
- Integrate Security Solutions: Utilize a layered approach by combining ID badges with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and biometric methods for enhanced protection.
These steps will help organizations navigate the evolving landscape of workplace identification technology while ensuring a secure environment for all employees.