3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing, prototyping, and product design. Whether for industrial applications or personal projects, this technology offers immense potential. However, one crucial element often overlooked in the 3D printing process is reverse engineering. Without it, replicating, improving, or repairing components efficiently becomes much more challenging. In this article, we will explore why reverse engineering 3D printing services play a vital role in the success of modern manufacturing and innovation.
Understanding Reverse Engineering in 3D Printing
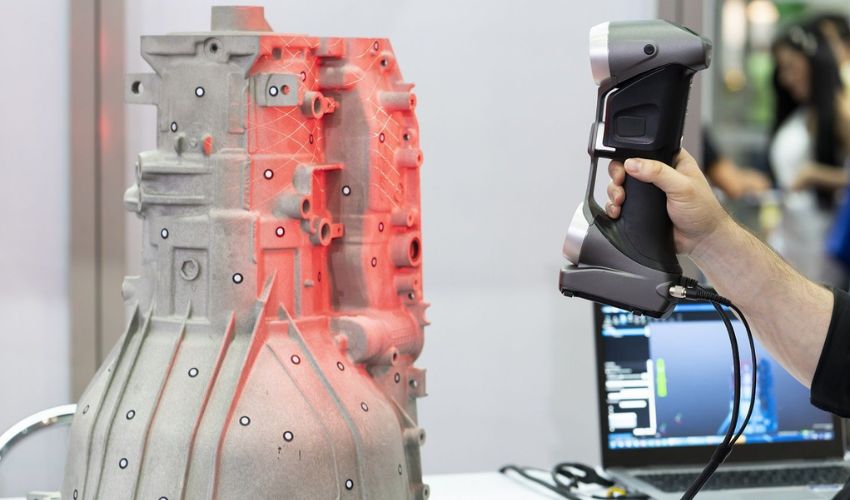
Reverse engineering is the process of deconstructing an object to understand its design, components, and functionality. In the context of 3D printing, this technique involves scanning, measuring, and analyzing existing parts to create precise digital models that can be reproduced or modified.
By using advanced 3D scanning technologies and software, engineers can convert physical objects into accurate digital blueprints. These files can then be used for various purposes, from replacing discontinued machine parts to customizing products based on real-world specifications.
The Importance of Reverse Engineering in 3D Printing
1. Replicating Obsolete or Hard-to-Find Parts
One of the most significant advantages of reverse engineering is its ability to recreate outdated or rare components. In industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, manufacturers often struggle to find replacement parts for aging equipment. Reverse engineering allows these essential parts to be reproduced without relying on original manufacturers, reducing downtime and costs.
2. Enhancing and Optimizing Existing Designs
Reverse engineering doesn’t just help with replication—it also enables product improvement. Engineers can analyze an object’s structure and modify it to enhance durability, efficiency, or functionality. This is particularly useful when working with older designs that may benefit from modern materials or streamlined geometries.
3. Reducing Manufacturing Costs
Conventional manufacturing techniques may call for costly molds and equipment. By reverse engineering an object and utilizing 3D printing, companies can significantly cut production costs. This is especially valuable for small-batch productions or custom components where traditional manufacturing would be cost-prohibitive.
4. Supporting Rapid Prototyping
Innovation thrives on iteration, and reverse engineering is an essential tool for rapid prototyping. By scanning an existing design, engineers can quickly make adjustments and print new versions without starting from scratch. This accelerates product development and minimizes material waste.
5. Enabling Customization
Reverse engineering allows manufacturers to tailor designs to specific customer needs. Whether it’s a custom medical implant, an ergonomic tool, or a unique automotive component, this process ensures precision and personalization. By capturing the exact dimensions and structures of real-world objects, 3D printing can produce highly customized solutions that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
The Reverse Engineering Process in 3D Printing
The reverse engineering workflow typically follows these steps:
- Object Scanning: A high-resolution 3D scanner captures the physical dimensions of an object. Various technologies, such as laser scanning and structured light scanning, ensure precision.
- Data Processing: The scanned data is converted into a digital format, usually a mesh file (STL) or CAD model.
- Design Modification: Engineers analyze and refine the model, correcting defects, optimizing features, or customizing the design.
- 3D Printing: Once the digital model is ready, it is sent to a 3D printer for fabrication using the appropriate material and printing technology.
- Quality Testing: The printed part is tested to ensure it meets performance requirements before being deployed.
Industries Benefiting from Reverse Engineering in 3D Printing
Aerospace & Automotive
In these industries, precision and reliability are critical. Reverse engineering helps manufacturers recreate discontinued parts, optimize aerodynamics, and enhance fuel efficiency by redesigning components with advanced materials.
Healthcare & Medical Devices
From prosthetics to dental implants, reverse engineering ensures that medical devices are customized to individual patients. This improves comfort, fit, and functionality while reducing production costs.
Manufacturing & Industrial Maintenance
Factories often face equipment failures due to outdated or unavailable parts. Reverse engineering enables the quick reproduction of these components, minimizing downtime and keeping operations running smoothly.
Consumer Products & Customization
Whether it’s creating a replica of a beloved but broken household item or customizing accessories, reverse engineering makes personalized manufacturing accessible to everyday consumers.
Overcoming Challenges in Reverse Engineering for 3D Printing
While reverse engineering offers numerous benefits, it does come with challenges. Achieving high accuracy in scanning, processing complex geometries, and ensuring material compatibility are some of the hurdles that need to be addressed. However, with advancements in scanning technology and AI-powered design tools, these challenges are becoming easier to overcome.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is an indispensable tool in modern 3D printing. It enables replication, innovation, cost savings, and customization across various industries. Without it, many opportunities for improvement and problem-solving would be lost. Whether for industrial applications or personal projects, leveraging reverse engineering 3D printing services ensures that businesses and individuals can make the most of this transformative technology. As 3D printing continues to evolve, reverse engineering will remain at the forefront of driving innovation and efficiency in the manufacturing world.