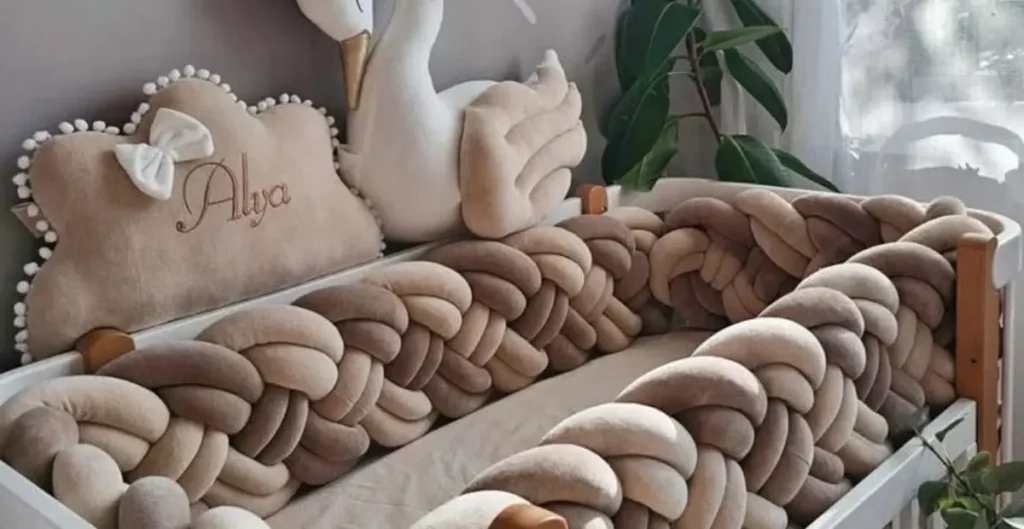
Crib bumpers can help create a cozy sleep area for babies, but choosing the right type is important for safety. Experts suggest using breathable mesh bumpers instead of thick padded ones to maintain airflow and reduce risks. A snug mattress and fitted crib sheet should always be the foundation of a safe sleep setup.
Modern crib bumpers that work focus on comfort without compromising safety. Look for lightweight, washable materials and simple designs that blend easily with your nursery theme. By choosing safe, breathable bumpers, you can create a calm and secure environment that supports peaceful sleep for your baby.
Why a Crib Bumper Matters for Baby Sleep
A well-chosen crib bumper can play a crucial role in enhancing your baby’s comfort and safety during sleep. Babies spend a significant portion of their early months in cribs, making the sleep environment essential for healthy development. A properly designed bumper protects infants from accidental bumps against crib rails while providing a gentle, cozy enclosure. Parents often focus on style, but safety and comfort must come first. High-quality crib bumper designs are breathable, hypoallergenic, and snugly fitted, ensuring infants can move freely without risk of entrapment. Beyond protection, bumpers can reduce startle reflexes and help babies feel secure, leading to longer, more restful sleep. By balancing safety, comfort, and design, parents can ensure that their nursery is both functional and visually appealing. Using a reliable crib bumper allows newborns to rest peacefully while giving parents confidence in their baby’s safety throughout the night.
Materials That Maximize Safety and Comfort
Selecting the right material is crucial when choosing a crib bumper. Soft, breathable fabrics like cotton, organic cotton, and bamboo provide airflow, reducing overheating and keeping the baby comfortable. Hypoallergenic padding helps prevent skin irritation, making the sleep surface safe for sensitive newborns. Natural materials are durable, soft, and gentle, even after multiple washes, ensuring long-lasting comfort.
Synthetic fabrics, although sometimes colorful or cheaper, are less breathable and may trap heat, potentially disturbing sleep. A high-quality crib bumper made of natural fabrics improves both safety and comfort, creating a cozy and secure sleeping environment. Parents who prioritize materials ensure their baby enjoys peaceful rest while reducing the risk of allergic reactions or discomfort. Proper material choice also enhances the durability and aesthetic appeal of the nursery setup.
Key Features to Look for in a Crib Bumper
Choosing the ideal crib bumper requires careful attention to safety, comfort, and practicality. Key features include:
- Breathable padding for proper airflow
- Snug-fitting design to prevent slipping or bunching
- Hypoallergenic materials for sensitive skin
- Durable stitching to withstand washing
- Machine-washable fabrics for easy cleaning
- Non-toxic dyes for infant safety
- Coordinated colors or patterns for nursery décor
These features help parents select a crib bumper that combines safety and style. High-quality bumpers reduce accidental injuries and provide a soft, protective boundary, ensuring babies sleep peacefully every night.
Safety Guidelines for Using Crib Bumpers
Safety is the primary concern when choosing a crib bumper. Loose, thick padding or improperly secured bumpers can pose a risk of suffocation or entrapment. Experts recommend using thin, breathable bumpers that fit snugly against the crib rails. Always check for non-toxic, fire-safe fabrics and avoid adding extra blankets or pillows inside the crib. A well-secured crib bumper provides protection without restricting movement, keeping the baby comfortable and safe. Parents should regularly inspect bumpers for wear and tear, ensuring they remain secure over time. Following safety guidelines ensures that bumpers contribute to a peaceful sleep environment without introducing hazards. Balancing aesthetics with strict safety standards allows parents to create a nursery that is both beautiful and functional.
Design Tips to Enhance Your Nursery
Crib bumpers are available in numerous colors, patterns, and themes, allowing parents to match them to the nursery décor. Soft pastels, neutral tones, and subtle prints create a calming environment, while bold designs or themed bumpers add personality to the room. Coordinated sets, including sheets, blankets, and bumpers, make the nursery visually appealing and organized. While design is important, it should never compromise safety or comfort. Choosing a crib bumper that combines style with functionality ensures the nursery is welcoming and practical. Parents can enjoy a space that is aesthetically pleasing while providing a safe and cozy sleeping environment for their newborn.
Types of Crib Bumpers
Understanding the types of crib bumpers helps parents select the best option for their baby’s nursery.
| Type | Best For | Key Benefit |
| Padded Bumper | Classic protection | Soft protection against rails |
| Breathable Mesh Bumper | Safety-conscious parents | Airflow and reduced suffocation risk |
| Quilted Bumper | Style-focused | Decorative and cozy |
| Organic Cotton Bumper | Sensitive skin | Hypoallergenic and natural |
| Modular Bumper | Custom crib setups | Flexible coverage and easy maintenance |
This table provides an overview of the most common options, helping parents make informed decisions when selecting crib bumpers for safety, comfort, and style.
Creating a Calming Sleep Environment
The overall sleep environment complements a crib bumper. Maintain a room temperature of 20–22°C to prevent overheating. Use blackout curtains or dim lighting to promote calm and relaxation. Keep the crib free from unnecessary toys, pillows, or blankets to reduce hazards. Pairing a quality crib bumper with these adjustments encourages longer, uninterrupted sleep. A peaceful nursery environment, combined with soft, protective bedding, supports the baby’s healthy development while giving parents reassurance and better rest. Consistent sleep routines further enhance the effectiveness of crib bumpers and improve nighttime comfort for infants and parents alike.
Cleaning and Maintaining Crib Bumpers
Proper care ensures crib bumpers remain safe, soft, and hygienic. Wash bumpers regularly using mild, fragrance-free detergent to remove dust, dirt, and allergens. Warm water cleans effectively without damaging the padding, and avoiding fabric softeners preserves breathability. Rotating multiple bumpers ensures clean sets are always ready.
Dry bumpers in sunlight when possible to maintain freshness and reduce bacteria. Store clean bumpers in a dry, dust-free area to preserve quality. Following these routines prolongs the life of crib bumpers, keeping them comfortable, safe, and visually appealing. Well-maintained bumpers ensure that the nursery remains inviting and functional for both babies and parents.
Conclusion
Selecting the right crib bumper is essential for balancing safety, comfort, and style in your baby’s nursery. Breathable, snug-fitting, and hypoallergenic designs provide protection while keeping the sleep environment cozy and safe. Coordinated colors and patterns enhance nursery aesthetics, and proper maintenance ensures durability and hygiene. By prioritizing function and style, parents can create a peaceful, secure, and visually appealing space for their newborn. Investing in high-quality crib bumpers guarantees restful nights, happier babies, and peace of mind for parents, making the nursery both safe and stylish.