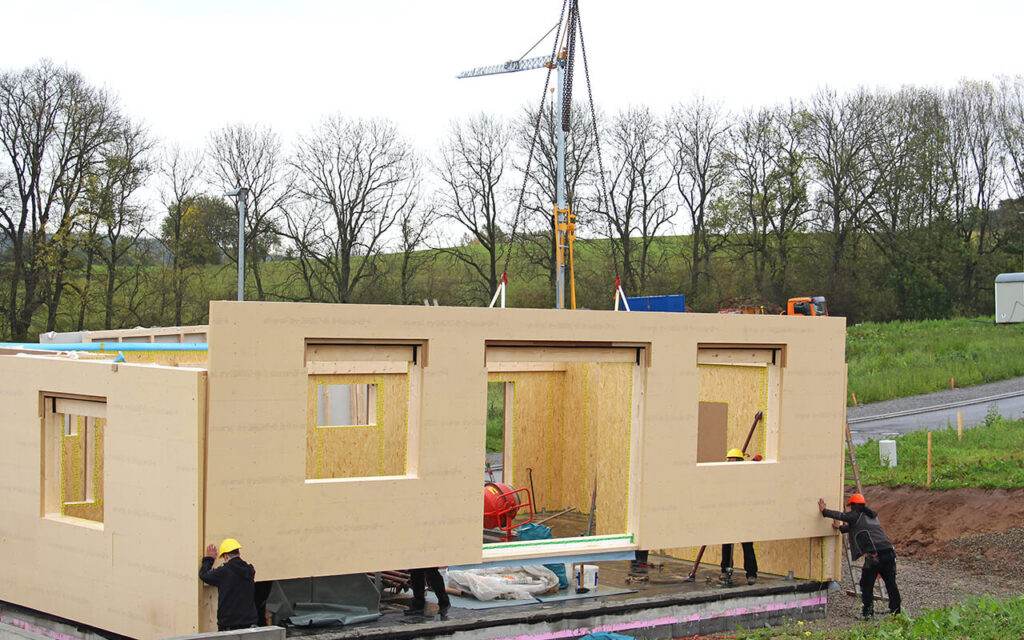
Innovations in construction have continually evolved to meet the demands of efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Among these advancements, prefabrication stands out as a transformative methodology. Prefabrication, often called off-site construction, involves assembling components in a factory or manufacturing facility before transporting them to the construction site for final assembly. This approach offers many possibilities, revolutionizing how structures are built across various sectors. The emergence of specialized prefab shops further amplifies the impact of prefabrication, providing dedicated spaces where customized components are meticulously crafted and assembled, ensuring precision and quality control throughout the construction process.
Efficiency Through Modularization
Prefabrication introduces a level of efficiency unparalleled in traditional construction methods. Manufacturing building components in a controlled environment significantly mitigates weather delays and on-site disruptions. This controlled environment allows for precise construction with minimal material waste, optimizing resources and reducing project timelines.
Modularization, an essential aspect of prefabrication, entails constructing individual modules or sections of a building off-site. These modules are then transported to the construction site and assembled, akin to assembling building blocks. This method expedites the construction process, allowing for concurrent activities such as site preparation and module fabrication. Consequently, project completion times can be reduced by up to 50%, offering substantial time and cost savings.
Enhancing Sustainability
Prefabrication aligns seamlessly with sustainable building practices, making it a compelling choice for environmentally conscious projects. A manufacturing facility’s controlled environment facilitates the implementation of eco-friendly measures such as optimized material usage, efficient energy consumption, and waste management practices.
Additionally, the modular nature of prefabricated components enables easier integration of sustainable technologies, such as solar panels, green roofs, and energy-efficient systems. By incorporating these features during the manufacturing phase, buildings can achieve higher levels of energy efficiency and environmental performance.
Prefabrication minimizes disturbance to surrounding ecosystems during construction, making it an ideal choice for projects in environmentally sensitive areas. With its reduced environmental footprint and ability to support green building initiatives, prefabrication emerges as a cornerstone of sustainable development in the construction industry.
Versatility Across Industries
The versatility of prefabrication extends beyond traditional building construction, encompassing various applications across industries. From residential and commercial buildings to infrastructure projects and temporary structures, prefabrication offers adaptable solutions tailored to diverse requirements.
In the healthcare sector, prefabricated modular units from reputed prefab shops have been utilized to rapidly deploy medical facilities, such as hospitals and clinics, particularly in emergencies or underserved areas. These modular healthcare facilities can be quickly assembled and customized to accommodate specific medical needs, providing timely access to essential services.
Similarly, the education sector has embraced prefabrication to address growing student populations and the need for flexible learning environments. Prefabricated classrooms and educational buildings offer schools a cost-effective and efficient solution to expand their facilities without the disruptions associated with traditional construction.
Prefabrication revolutionizes the construction of bridges, tunnels, and transportation facilities. Off-site fabrication of structural elements accelerates project timelines and enhances safety by reducing on-site construction activities in high-risk environments.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While prefabrication presents numerous benefits, it has its challenges. Design complexity, transportation logistics, and regulatory compliance are among the elements that require careful consideration when implementing prefabricated solutions. However, technological advancements, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and digital fabrication techniques, are helping overcome these challenges by streamlining the design-to-manufacturing process and enhancing collaboration among project stakeholders.
The future of prefabrication appears promising as innovation continues to drive its evolution. Emerging trends such as 3D printing of building components, robotic automation in manufacturing, and using sustainable materials present exciting opportunities to enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and versatility of prefabricated construction further.
In conclusion, prefabrication represents a significant leap forward in construction, merging efficiency, sustainability, and versatility. By transforming traditional building practices through off-site manufacturing and modularization, it addresses contemporary challenges of time, cost, and environmental impact. As the industry evolves, with advancements in technology and materials, prefabrication stands poised to redefine the construction landscape, promising a future where projects are realized more swiftly, sustainably, and flexibly than ever before.